Markov Chains, Rewards & Rules
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction and Related Work
-
Methodology
2.1 LLM-Sim Task
2.2 Data
2.3 Evaluation
-
Experiments
-
Results
-
Conclusion
-
Limitations and Ethical Concerns, Acknowledgements, and References
A. Model details
B. Game transition examples
C. Game rules generation
D. Prompts
E. GPT-3.5 results
F. Histograms
2 Methodology
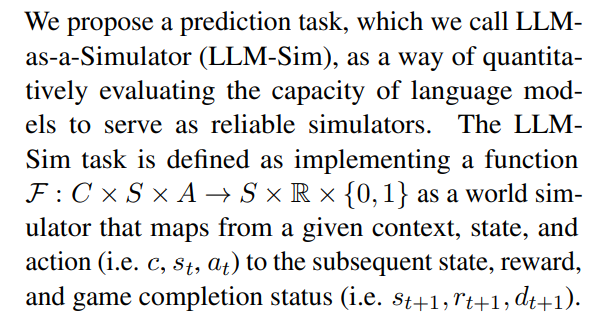
We examine the abilities of LLMs to serve as world simulators in text-based virtual environments, in which an agent receives observations and proposes actions in natural language in order to complete certain objectives. Each text environment can be formally represented as a goal-conditioned partially observable Markov decision process (POMDP) (Kaelbling et al., 1998) with the 7-tuple (S, A, T , O, R, C, D), where S denotes the state space, A denotes the action space, T : S × A → S denotes the transition function, O denotes the observation function, R : S × A → R denotes the reward function, C denotes a natural language “context message” that describes the goal and action semantics, and D : S × A → {0, 1} denotes the binary completion indicator function.
\ 
\
2.1 LLM-Sim Task
\ 
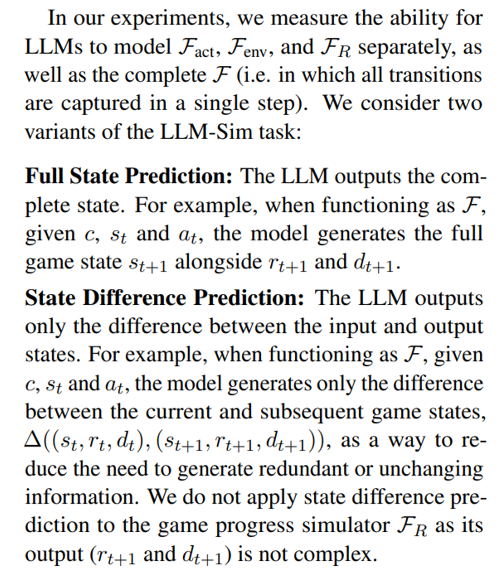
\ \ In practice, the whole state transition simulator F should consider two types of state transitions: action-driven transitions and environment-driven transitions. For the example in Figure 1, the action-driven transition is that the sink is turned on (isOn=true) after taking the action turn on sink, and the environment-driven transition is that water fills up the cup in the sink when the sink is on. To better understand LLM’s ability to model each of these transitions, we further decompose the simulator function F into three steps:
\ \ 
\ \ \ 
\
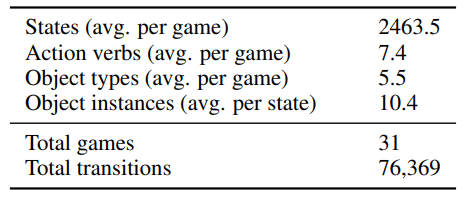
2.2 Data
\ 
\ \ Additional Context: Each game also includes a context message, c, that provides additional information to the model. The context consists of four parts: action rules describing the effect of each action on the game state, object rules describing the meaning of each object property and whether they are affected by the game’s underlying dynamics, scoring rules describing how an agent earns reward and the conditions under which the game is won or lost, and one or two example transitions (see Appendix B for details) from the held-out game mentioned above. For each game we generate three
\ \ 
\ \ \ 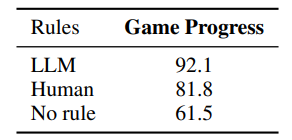
\ \ versions of the context, one where the rules are written by a human expert (one of the game authors), and one where they are produced by an LLM with access to the game code, and one where no rules are provided. See Appendix C for additional details.
\
2.3 Evaluation
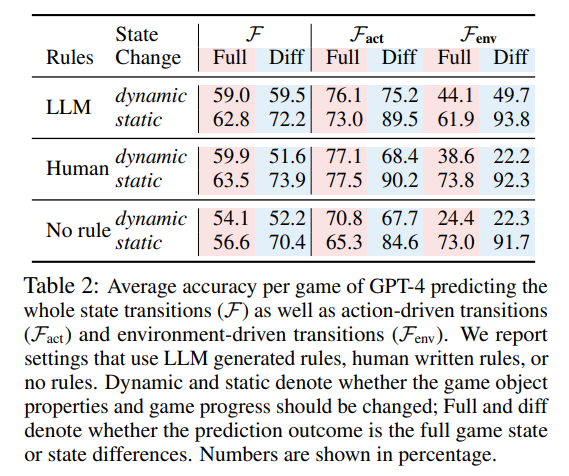
Performance on LLM-Sim is determined by the model’s prediction accuracy w.r.t. the ground truth labels over a dataset of test samples. Depending on the experimental condition, the LLM must model object properties (when simulating Fact, Fenv, or F) and / or game progress (when simulating FR or F), defined as:
\ Object Properties: a list of all objects in the game, along with each object’s properties (e.g., temperature, size) and relationships to other objects (e.g., being within or on top of another object).
\ Game Progress: the status of the agent w.r.t. the overall goal, consisting of the current accumulated reward, whether the game has terminated, and whether the overall goal has been achieved.
\ \ 
\ \ \
:::info Authors:
(1) Ruoyao Wang, University of Arizona ([email protected]);
(2) Graham Todd, New York University ([email protected]);
(3) Ziang Xiao, Johns Hopkins University ([email protected]);
(4) Xingdi Yuan, Microsoft Research Montréal ([email protected]);
(5) Marc-Alexandre Côté, Microsoft Research Montréal ([email protected]);
(6) Peter Clark, Allen Institute for AI ([email protected]).;
(7) Peter Jansen, University of Arizona and Allen Institute for AI ([email protected]).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

XRP Price Prediction: Ripple CEO at Davos Predicts Crypto ATHs This Year – $5 XRP Next?

Fed Decides On Interest Rates Today—Here’s What To Watch For

