LLMs + Vector Databases: Building Memory Architectures for AI Agents
The Memory Challenge: Why Agents Need More Than Raw Compute
Machine learning models that handle inputs and outputs in separate formats and files are familiar to data scientists and experts. As in most situations, AI agents are needed to maintain context, learn from interactions, and access massive knowledge stores that no model can handle, requiring a fundamental transformation.
\ Think about the figures: The 128k token limit for GPT-4 is equivalent to about 96,000 words. This limitation becomes a major barrier for a research assistant dealing with whole academic libraries or a customer service representative managing thousands of transactions every day. Smarter memory architectures, not larger context windows, are the answer.
\ This is where vector databases become essential infrastructure, transforming the fuzzy problem of "semantic memory" into the precise domain of high-dimensional similarity search that we understand as data scientists.
From Feature Engineering to Semantic Embeddings
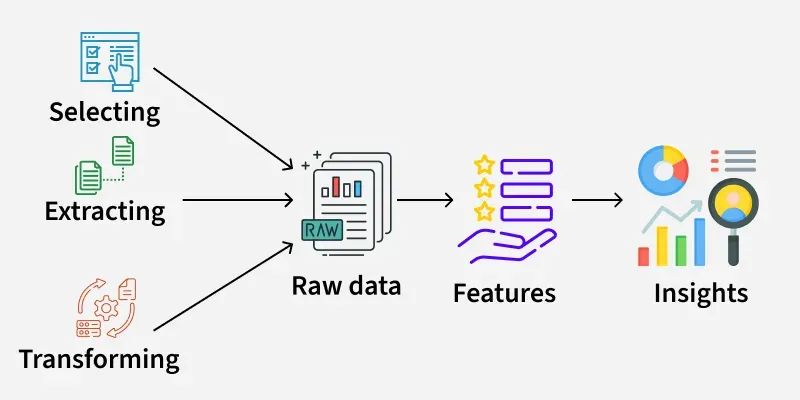
Embeddings are the first step in the big idea jump from standard machine learning to agent memory systems. Modern embedding models are like smart feature extractors that turn normal language into rich, meaningful representations.
\ Neural embeddings represent semantic links in continuous space, unlike sparse, fragile features like TF-IDF and n-grams. OpenAI's text-embedding-3-large transforms "machine learning model deployment" into a 3072-dimensional vector with cosine similarity that meets human semantic relatedness evaluations.
\ We have converted qualitative similarity ("these documents are about similar topics") into quantifiable distance measurements that we can measure, optimize, and systematically improve. This is a major data science understanding.
Vector Databases: The Infrastructure Layer
Vector databases solve the scalability challenge that emerges when you need to search millions of high-dimensional embeddings in real-time. As data scientists, we can think of them as specialized OLAP systems optimized for similarity queries rather than aggregations.
\ The core technical challenge mirrors problems we've solved in other domains: how do you efficiently search high-dimensional spaces without exhaustive comparison? The curse of dimensionality renders traditional tree-based indexes (KD-trees, Ball trees) useless when the number of dimensions exceeds about 20.
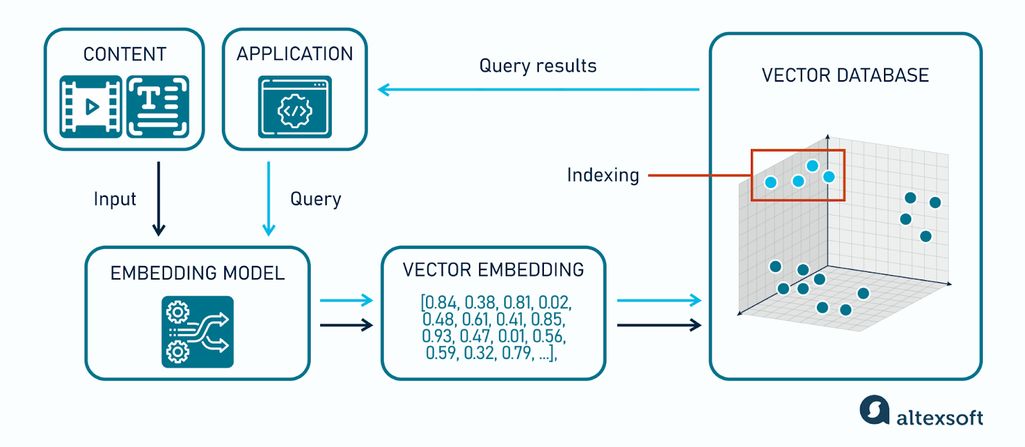
Modern vector databases employ sophisticated indexing strategies:
- HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World): A multi-layer graph is constructed, in which every node is connected to its closest neighbors. This is primarily because the search complexity scales logarithmically, and also requests with millions of vectors, which in most cases, may still be completed in less than 100ms.
- IVF-PQ (Inverted File with Product Quantization): By clustering the vector space and employing learnt compression, this reduces the memory footprint by 75% while preserving strong recall. This is a classic precision-recall optimization that we know from ML model tweaking, where some accuracy is traded for huge scalability.
\ The factors that influence the choice between these approaches involve familiar data science trade-offs: latency vs. throughput, memory vs. accuracy, and cost vs. performance.
Memory Architecture: Episodic vs. Semantic Storage
Drawing from cognitive psychology research, effective agent memory systems implement dual storage mechanisms that mirror human memory patterns:
- Episodic Memory stores raw, timestamped interactions, which are not limited to attributes such as every conversation turn, tool execution, and environmental observation. This provides perfect recall for debugging, audit trails, and context reconstruction. From a data science perspective, think of this as your "raw data lake" where nothing is lost or transformed.
- Semantic Memory contains distilled, structured knowledge extracted from episodic experiences. It is at this point where agents store learned facts about users, domain knowledge, and behavioural patterns. Analogous to feature stores in ML pipelines, semantic memory provides fast access to processed insights.
\ The key insight is that these aren't just different databases; they serve different analytical purposes and have different retention, update, and query patterns.
Frameworks Used for Experimental Design and Evaluation
All acceptable experiments must be done with utmost care and precision, in order to make agents with memory systems that work and produce expected results, which is a good fit for data science methods. Some important aspects of review are:
- Retrieval Quality: Use human-labelled relevance ratings to measure recall@k and Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR). For this article, instead of us making general guesses and measurements, we would make test sets that describe how the agent should actually handle queries.
- From Beginning to End Performance: In our case, we keep track of how many tasks are completed, and we also check to see how satisfied users are, including how well responses are made. To measure changes in answer quality, use tools such as BLEU, ROUGE, or semantic similarity metrics.
- System Performance: Keep an eye on how much it costs to install, how much storage grows, how query delay is spread out, and how infrastructure grows. These practical metrics are often more important than pure accuracy measures for figuring out if a production can go ahead.
- Ablation studies: These ensure to change the embedding models, chunk sizes, recovery methods, and context compression techniques in a planned way. This helps figure out which parts lead to better speed and where to put your tuning efforts.
Patterns and Strategies for Improving Performance
- Hybrid retrieval: Using this retrieval method, we make sure that the dense vector starts a search and sparse keyword matching using the (BM25) to get good results for all kinds of queries. We know this pattern from model stacking: this group approach often works better than either way by itself.
- Dynamic Context Allocation: Set up learned rules that change how the context window is used based on the complexity of the query, the user's past, and the needs of the job. This turns allocating static resources into an efficiency problem.
- Making small changes: Use contrastive learning on agent-specific data to adapt general embedding models to your area. Models that are already on the market might not be 15–30% more accurate than this one.
Thoughts on Making Things and Having Trouble Scaling
-
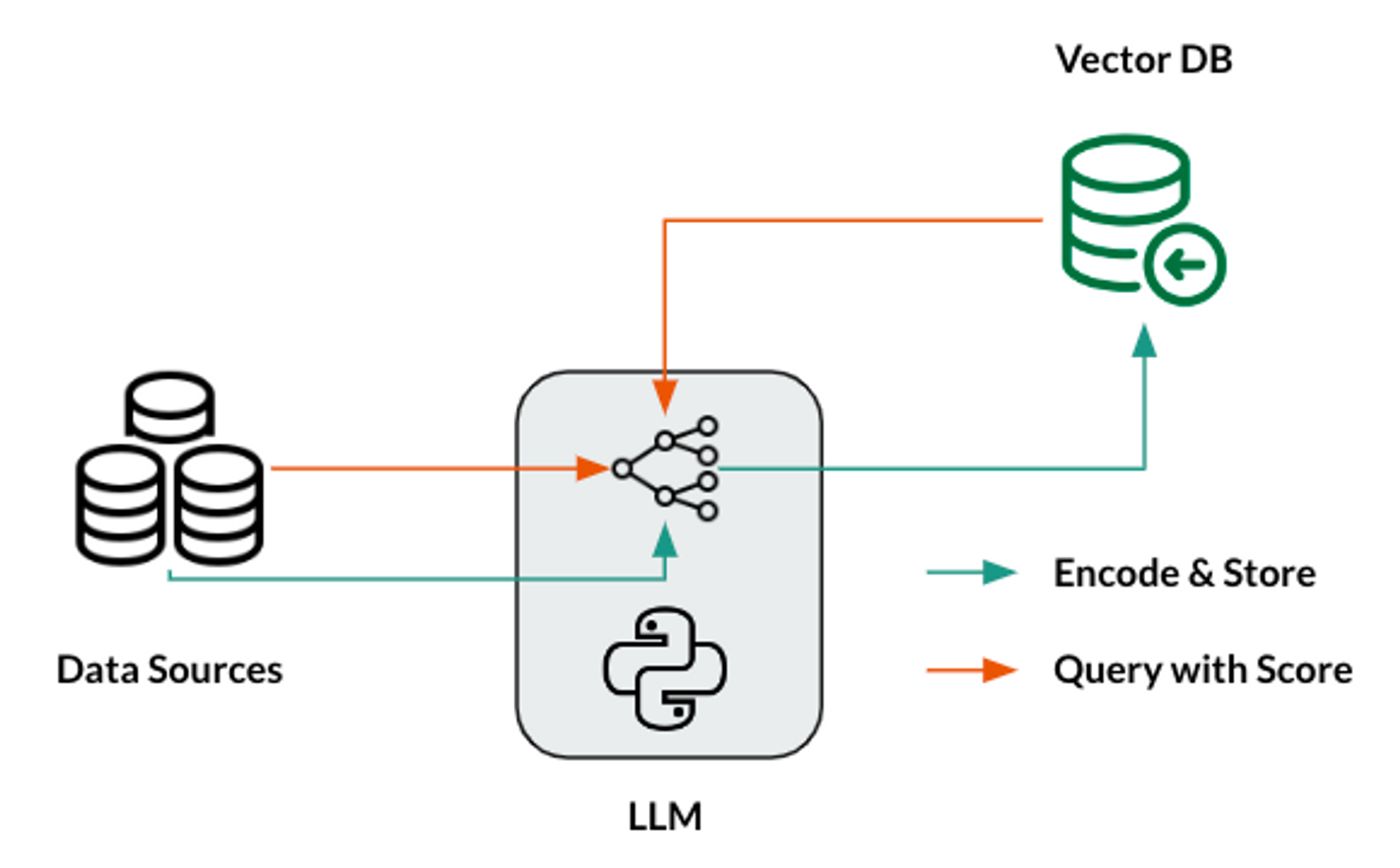
Manage costs: Putting APIs in text makes the costs go up straight with the amount of text. Smart chunking plans, compression methods, and the careful addition of high-value content should all be put in place. Watch how much it costs per contact and set up alerts to let you know when you go over your limit.
-
Quality of Data: Vector systems make issues with the quality of data worse. For instance, chunking that doesn't work right, style that isn't even, or text that is tough to read all slow down the system. Now, also ensure to track the result quality and ensure that the data is appropriately using pipelines that work like ML feature pipelines.
-
Safety and Security: Embeddings keep track of what the source text means, which could be a safety risk. You should think about different privacy settings, access controls, and rules for saving data that are both useful and legal.
\
What This Means for Strategy
Vector databases are the foundation of emerging smart systems that learn and adapt. Data scientists creating AI bots use them more than simply tools.
\ Using our logical skills, we can create an agent memory to monitor systems, coordinate testing, and speed things up. System development and difficulty are the greatest changes. Instead of improving one model, we're building distributed systems with several AI parts that work together.
\ This change is akin to the move from group-learning AI systems to always-together AI systems. These memory structures must be understood by a data scientist to govern future AI algorithms. These applications use bots repeatedly to help users learn.

You May Also Like

Where Next for Bitcoin? The Bull and Bear Case

The million-dollar winner of the X Creators Contest has been exposed for involvement in a Memecoin scam.
