Bittensor (TAO) Explained: A Trillion-Dollar Market Opportunity
Author: hitesh.eth , Crypto KOL
Compiled by Felix, PANews
This article delves into Bittensor, explaining why it is not a decentralized OpenAI, but rather a decentralized AI economy; it also explains how dTAO reshapes incentive mechanism design, how subnet economies work, and why TAO represents a cultural resistance to centralized AI.
What changed after dTAO?
Many may be wondering what Bittensor is trying to achieve. Is it trying to create a decentralized OpenAI, or is there something deeper at play? In fact, the crypto community generally believed that it could be a decentralized OpenAI, but confusion arose when it removed subnet restrictions and introduced the dTAO (which also involved subnet tokens) to make it more competitive. This shift was crucial because it shifted the network's reward distribution from centralized voting by a small number of validators to a fully market-driven system.
The introduction of dynamic TAOs (dTAOs) fundamentally changed the ecosystem's operating mechanisms. The allocation of daily TAO issuance shifted entirely from the root validator (Subnet 0, which critics called an oligarchic voting system) to the market price of each subnet's alpha token. Each mining subnet received its own alpha (α) token and its own automated market maker (AMM) pool. This enabled each subnet to develop an independent, capital-driven economy. Staking shifted from delegating TAOs to a single validator (Subnet 0 staking) to purchasing and staking subnet-specific alpha tokens (α). Stakers now bear market risk but can directly influence resource allocation. The previously rigid 50/50 reward split between miners and validators evolved to the current 41/41/18 split to better fund subnet owners (18%) and encourage continued innovation in the subnet's core incentive mechanisms.
Grand Vision
Today, Bittensor competes with centralized AI development and distribution platforms, providing developers with the infrastructure to build diverse AI use cases across various industries. This is crucial to understanding Bittensor's total addressable market (TAM). While companies like OpenAI compete in the multi-billion dollar immediate market, selling finished AI products like subscriptions or API access, Bittensor targets the multi-trillion dollar market for the entire AI value chain—including computing infrastructure, data validation, model training, and the peer-reviewed intelligence layer.
If successful, Bittensor, as the foundational, permissionless platform for all decentralized AI, will have a TAM far exceeding that of any single proprietary AI company. Bittensor is developing and deploying diverse AI models, building a coordination engine for a distributed and decentralized AI ecosystem while simultaneously incentivizing the provision of funding and computing resources to achieve the highest levels of quality, efficiency, and trust in outcomes across decentralized AI projects for diverse use cases. This is more like building a decentralized AI value chain in which anyone can participate with capital, knowledge, and computing power.
Bittensor is for everyone, not just the 0.000001% of the world who can participate in OpenAI.
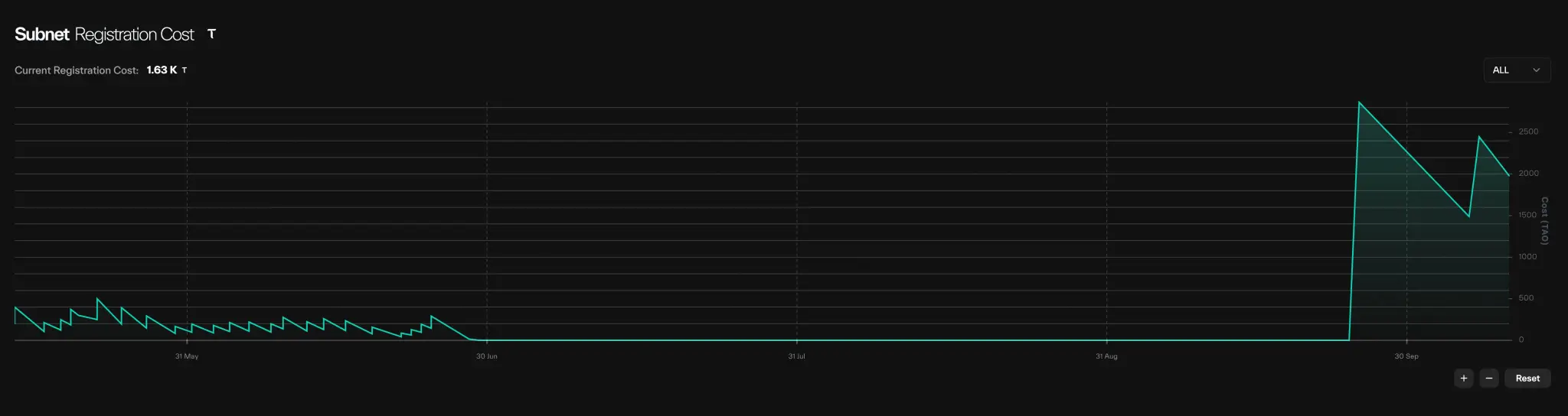
Bittensor's overall vision is to build a neural internet. Over the past four years, Bittensor has built a loyal community that brings together top VCs like DCG, crypto researchers like Sami Kasab, and many talented people who work every day to advance this vision. They create content, do podcasts, develop products, and are starting a movement. Bittensor has also built a subnet ecosystem, with approximately 126 subnets currently active. The current cost of a subnet is approximately 1,600 TAOs ($640,000 USD), and this cost is dynamic and will change based on the frequency of new subnet registrations. After a few months of suspension, new subnet registrations are now open again.
Grayscale, founded in 2013 by Barry Silbert, one of the earliest Bitcoin pioneers, aimed to attract institutional investors to Bitcoin. Now, Grayscale is creating a similar fund for subnet tokens. The fund, called the Yuma Subnet Composite Fund, will invest in the top subnet tokens by market capitalization.
Subnet Tokens
Subnet tokens are currently one of the most overlooked assets on crypto Twitter. 99% of users are completely unaware of this space. The core concept behind subnet token prices is that they are denominated in TAO, rather than simply pegged, and are determined by the liquidity ratio in their automated market maker (AMM) pools. The higher the value of a subnet token relative to TAO, the more it is issued. More issuance attracts more miners to host and run AI models and provide computing resources. Miners compete to optimize the output of subnet models, and better results lead to higher prices. More precisely, better service attracts more staking demand, which drives up prices, ensuring the overall output quality of AI models used in different subnets for different use cases. Validators ensure that miners maintain quality.
Their job is to verify the miners' work and assign a score to it. Based on this score, the miners receive issuance from the subnet. Approximately 7,200 TAOs are issued daily, and this number will be halved over the next two months, with the first Bittensor halving event in December.
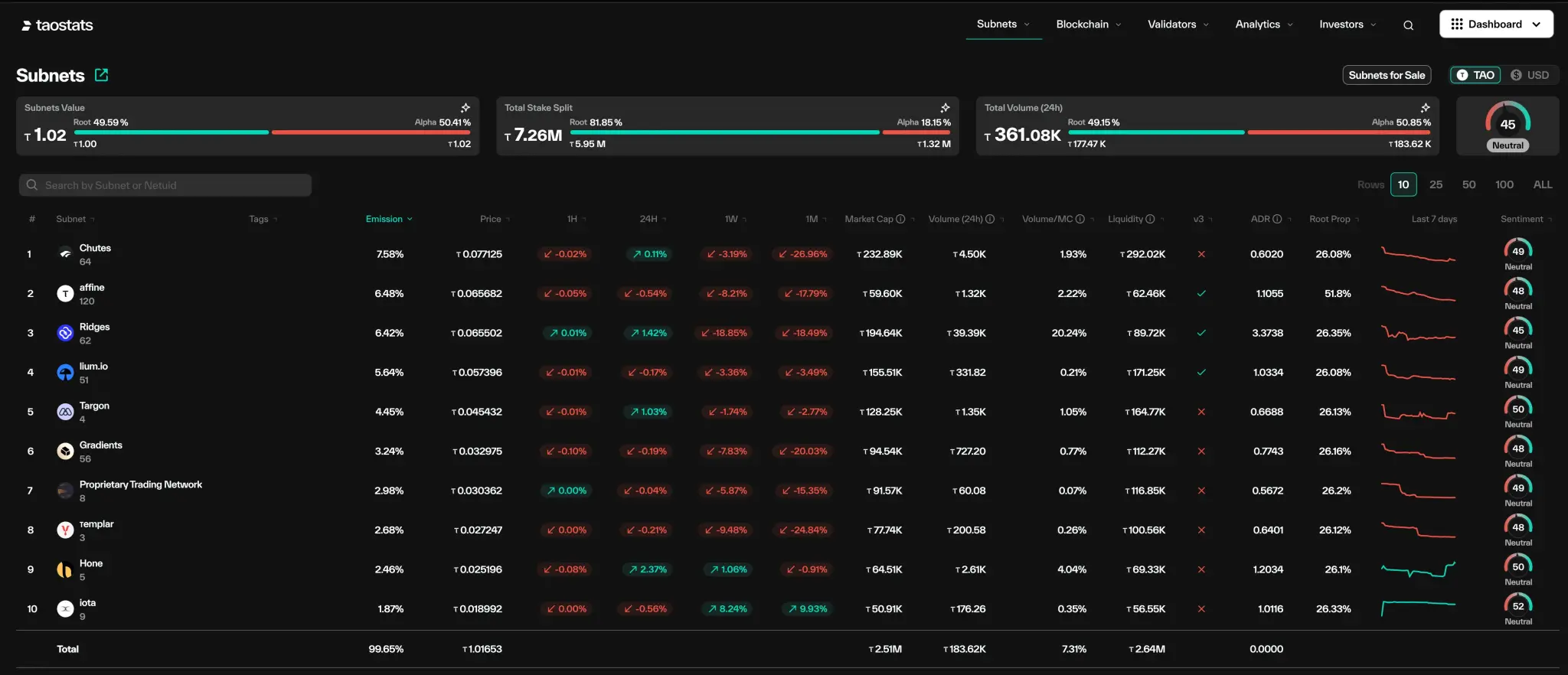
This means there's currently intense competition within the mining ecosystem for the highest returns. Most miners will stick to mining on the best-performing subnets, and if they mine on top subnets, the price of those subnet tokens will rise accordingly. Increased mining demand driven by high issuance always leads to higher subnet token prices. Initial demand for mining on a subnet often comes from speculation about the use case it's building, the team behind it, its track record, and the backing of a major corporation.
Currently, the top subnet tokens with the highest issuance volume include Chutes, Ridges, and Gradient. Some of these subnets are also venture-backed. For example, Gradient is building the AI Trains platform. It was built by Rayon Labs, which also operates Chutes, the leading subnet by issuance volume. Many of these subnets are collaborating with each other to exchange services. For example, Ridges is a Chutes client; Sportstensor is building AI models for sports betting and prediction; and there are subnets like OpenKaito, which powers Kaito's InfoFi Pioneer. Taofi is also part of Bittensor. They have launched a DEX that allows you to easily bridge and exchange subnet tokens from the Base network.
Trust TAO
If you're asking which subnet tokens will attract demand, you need to track the growth of the subnet token's price relative to TAO. The more growth you see over different timeframes, the higher the demand. Then, you need to look at the ADR (alpha distribution ratio). It should be less than 1, as token withdrawals are now permitted. The worst-performing subnets are withdrawn weekly. If the ADR ratio is above 1, the community may lose a portion of the value of the TAO collateral staked to acquire that token due to the liquidation discount upon withdrawal.
You can also track staking pools for different subnets. The more TAO is staked to acquire subnet tokens, the more likely the price will rise. Therefore, the value of subnet tokens depends largely on how long they can maintain high issuance. If they maintain high issuance and the businesses surrounding the subnet generate revenue from the services and products they provide, the price of the subnet token is likely to continue to rise. The overall market capitalization growth surrounding the subnet will directly drive TAO price increases.
However, it's recommended to stay away from things you don't understand. Subnet tokens aren't like your average altcoin or junk coin. They require a deeper logical understanding, so if you believe in their vision, invest in TAO. TAO isn't meant to be traded, but rather a cultural symbol against AI centralization.
The question isn’t whether decentralized AI will exist, but who will own it. Bittensor has made its choice, and others will too.
Related Reading: Bittensor Subnet Investment Guide: Seizing the Next AI Trend
You May Also Like

UK To Deepen Crypto Ties With US, May Adopt More Pro-Crypto Approach: FT

Coinbase Issues Cryptocurrency Call to US Justice Department: “Solve Urgent Problems!”

