Bybit security investigation reveals the truth: SAFE front-end cloud service was attacked, how to ensure the safety of hundreds of billions of assets carried by multi-signature wallets
Author: Frank, PANews
On February 21, 2025, the cryptocurrency exchange Bybit suffered an epic hacker attack, and assets worth $1.46 billion were stolen by the North Korean hacker group Lazarus. In addition to recovering the assets, it is more important to identify the attack path to avoid new attacks. On February 27, Bybit released a hacker forensics report, and the investigation directly pointed out that the theft of funds was caused by a vulnerability in Safe's infrastructure. But it seems that Safe is unwilling to accept this accusation. In the statement, it admitted that the developer was hacked, but attributed the main reason to the clever methods of North Korean hackers and Bybit's operational errors. The "Rashomon" was staged in the discussion of who is more responsible, which also triggered a big debate in the industry on infrastructure trust, security paradigms and human nature.
The attack originated from the attack on Safe{Wallet} front-end cloud service
According to two investigation reports released by Bybit (Bybit Incident Preliminary Report and Bybit Interim Investigation Report), further analysis of Safe{Wallet} resources found two JavaScript resource snapshots taken on February 19, 2025. Review of these snapshots showed that the first snapshot contained the original, legitimate Safe{Wallet} code, while the second snapshot contained resources with malicious JavaScript code. This suggests that the malicious code that created the malicious transaction originated directly from Safe{Wallet}'s AWS infrastructure.
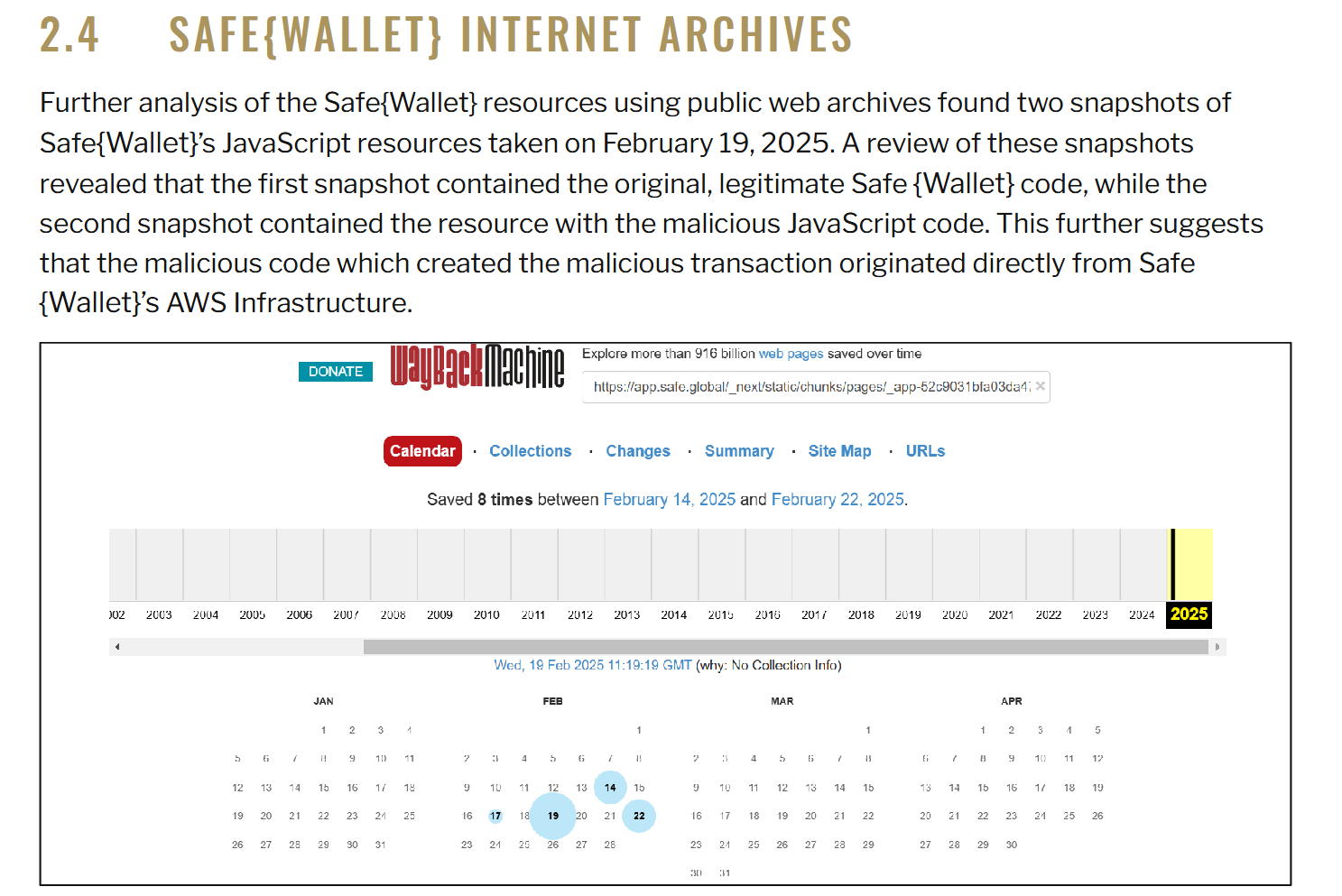
The report's conclusion reads: Based on our findings on Bybit's signer machines and the cached malicious JavaScript payloads found in the Wayback Archive, we strongly conclude that Safe.Global's AWS S3 or CloudFront account/API keys may have been compromised.
To summarize briefly, the initial source of this attack was that hackers attacked the Safe{Wallet} developer's device, tampered with the front-end JavaScript file in the AWS S3 bucket, and implanted targeted malicious code targeting the Bybit cold wallet address. Previously, Safe also released a simple investigation report, stating that no code vulnerabilities and malicious dependencies (i.e., supply chain attacks) were found. Safe then conducted a comprehensive review and suspended the Safe{Wallet} function. The results of this investigation seem to overturn Safe's previous investigation results.
Safe's evasive statement raises more questions
Bybit has not yet stated what responsibility Safe should bear in this incident, but after the report was released, people on social media began to discuss Safe's security vulnerability and some believed that Safe should be held responsible and make compensation.
Safe's official attitude towards this report is obviously not recognized. In its official statement, Safe divides the responsibility into three levels: in terms of technology, it emphasizes that the smart contract has not been attacked and emphasizes the security of the product. In terms of operation and maintenance, it admits that the developer's device was hacked and caused the AWS key to be leaked, but blames it on the national attack of the North Korean hacker organization. In terms of users, it recommends users to "be vigilant when signing transactions", implying that Bybit did not fully verify the transaction data.
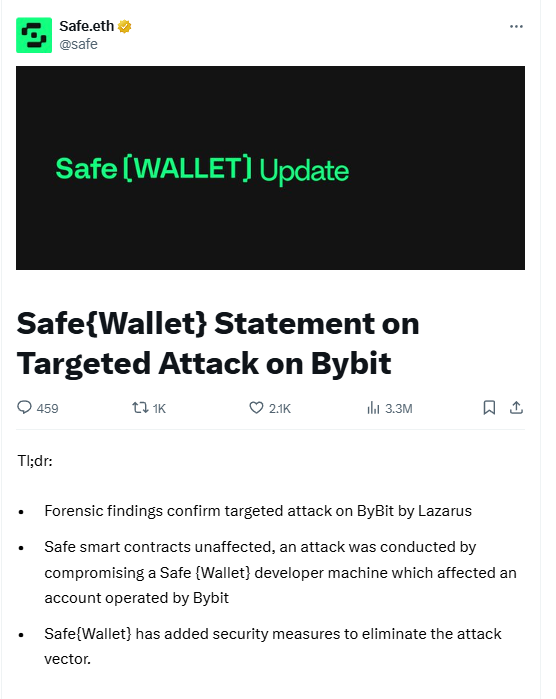
However, this response seems to be evasive. According to the process shown in the report, Safe has the following negligence in this process:
1. Loss of control over permissions: Attackers gained AWS permissions by hacking into developers’ devices, exposing that the Safe team did not implement the principle of least privilege. For example, a developer could directly modify the production environment code without a code change monitoring mechanism.
2. Front-end security failure: basic protection measures such as SRI (subresource integrity verification) were not enabled.
3. Supply chain dependency risk: The attack path (developer device → AWS → front-end code) proves that Safe is overly dependent on centralized cloud services, which conflicts with the decentralized security concept of blockchain.
In addition, the industry has also raised many questions about Safe's statement. Binance founder CZ has raised five technical questions in a row (such as the specific way the developer's device was hacked, the reason for the loss of control of permissions, etc.), directly pointing out the information opacity of Safe's statement. Safe did not disclose the details of the attack chain, resulting in the industry being unable to take targeted defenses.
Tokens rose strangely, and daily activity dropped by nearly 70%
Another major point of contention in the community is whether Safe should compensate Bybit for the losses in this incident. Some users believe that the attack was caused by a vulnerability in Safe's infrastructure, and Safe should be responsible for compensation. What's more, it is proposed that Gnosis, the predecessor of Safe, bear joint and several liability for compensation. Safe was originally developed as a multi-signature agreement by the Gnosis team in 2017 as Gnosis Safe, and was spun off from the Gnosis ecosystem in 2022 to operate independently. Gnosis completed an ICO financing of 250,000 ETH in 2017, and currently has 150,000 ETH in its treasury, which belongs to the ETH whale.
However, some people believe that the main responsibility for this incident lies with Bybit itself. On the one hand, it is necessary to invest in research and development to develop a series of security infrastructures in order to manage cold wallets with more than one billion assets. On the other hand, Bybit seems to use the free Safe service and does not pay a subscription fee, so Safe has no obligation to bear responsibility from this perspective.
After publishing the investigation report, Bybit did not ask Safe for financial compensation.
While the industry is still arguing about who should be held responsible, the capital market is playing out an absurd drama. Safe's official token seems to have received special attention because of this incident. On February 27, the SAFE token rose against the trend from $0.44 to $0.69, with a maximum increase of about 58% in 10 hours. However, from an investment logic perspective, the incident has mainly had a negative impact on Safe's brand, and the rise may only be due to short-term market sentiment.
Data on February 27 showed that Safe's total managed assets exceeded US$100 billion, and its silence on the details of the vulnerability is shaking its credibility as industry infrastructure.
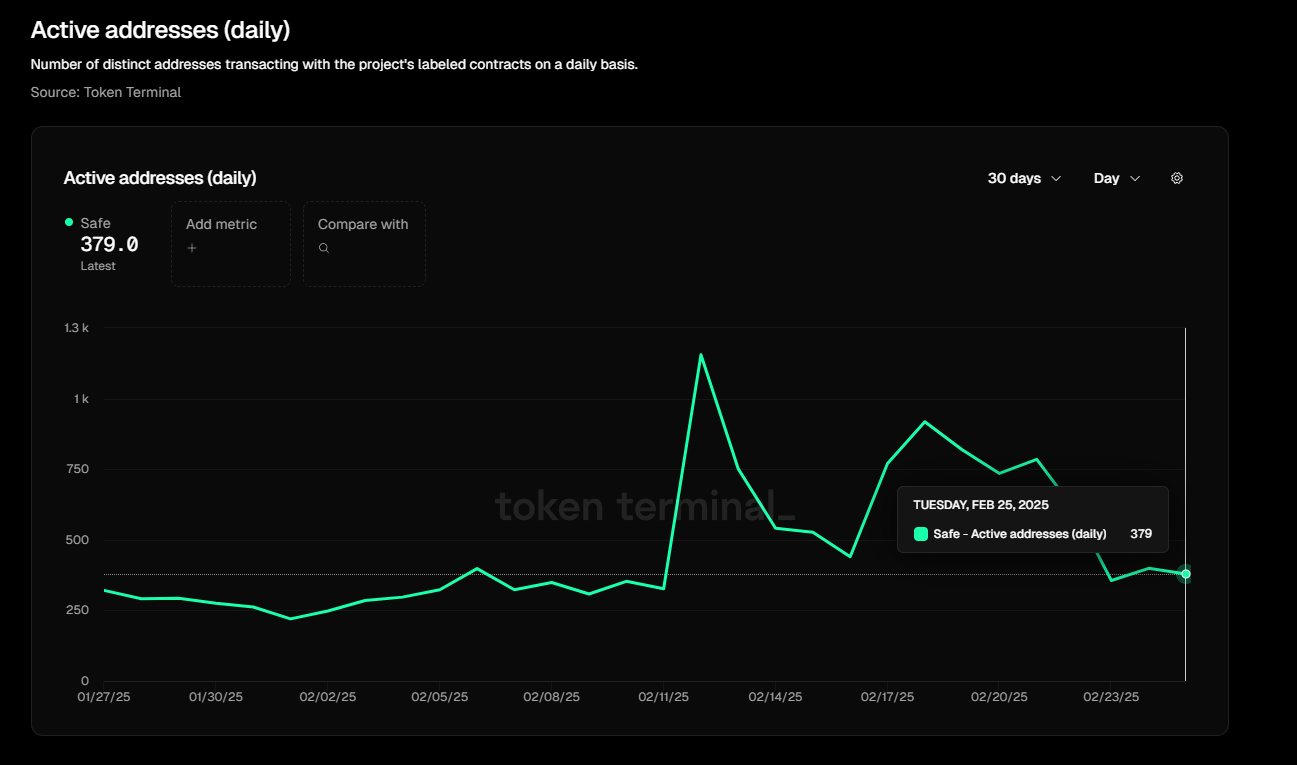
From the daily active user data, it can be clearly seen that Safe suffered a considerable impact after this incident. Compared with the 1,200 daily active addresses on February 12, the data dropped to 379 daily active addresses on February 27, a decrease of nearly 70%.
 In addition, after the centralization risk of the front-end was exposed, the community once again paid attention to the security mechanism of the front-end. Dominic Williams, founder of ICP, said that the North Korean hacker group recently successfully stole $1.5 billion in funds from Bybit, mainly by exploiting the web-side vulnerability of Safe{Wallet}, which is hosted on the cloud rather than on smart contracts. Williams criticized some Web3 projects for running only on a "fake onchain", which leads to security risks, and suggested using ICP (Internet Computer) for on-chain computing, data storage, and user experience verification to improve security. He proposed that Safe{Wallet} be migrated to ICP and adopt encrypted authentication mechanisms and multi-party consensus governance (such as SNS DAO) to enhance security.
In addition, after the centralization risk of the front-end was exposed, the community once again paid attention to the security mechanism of the front-end. Dominic Williams, founder of ICP, said that the North Korean hacker group recently successfully stole $1.5 billion in funds from Bybit, mainly by exploiting the web-side vulnerability of Safe{Wallet}, which is hosted on the cloud rather than on smart contracts. Williams criticized some Web3 projects for running only on a "fake onchain", which leads to security risks, and suggested using ICP (Internet Computer) for on-chain computing, data storage, and user experience verification to improve security. He proposed that Safe{Wallet} be migrated to ICP and adopt encrypted authentication mechanisms and multi-party consensus governance (such as SNS DAO) to enhance security.
Looking back at the entire incident, it seems to be an isolated incident carefully planned by North Korean hackers, but it still exposes the security loopholes in the permission design and supply chain of Safe's current multi-signature wallet. From the perspective of brand development, the practice of rushing to distance oneself from the issue in order to deliberately maintain the safety myth is counterproductive and has instead triggered more doubts from the public. Perhaps, Safe's timely admission of mistakes and the introduction of corresponding measures can better reflect the attitude of a giant in the field of cryptographic security. At the same time, publishing the details of the vulnerability as soon as possible can also further help the industry strengthen self-inspection and prevention of similar vulnerabilities.
You May Also Like

‘Huge’ investor demand for apartment buildings

Trump has 'collapsed' with 'core voters' on 3 key issues
