How Weekly AI Training Is Beating a Nobel Prize-Winning Formula
:::info Authors:
(1) Reilly Pickard, Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada ([email protected]);
(2) F. Wredenhagen, Ernst & Young LLP, Toronto, ON, M5H 0B3, Canada;
(3) Y. Lawryshyn, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
:::
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
Similar Work
3.1 Option Hedging with Deep Reinforcement Learning
3.2 Hyperparameter Analysis
-
Methodology
4.1 General DRL Agent Setup
4.2 Hyperparameter Experiments
4.3 Optimization of Market Calibrated DRL Agents
-
Results
5.1 Hyperparameter Analysis
5.2 Market Calibrated DRL with Weekly Re-Training
-
Conclusions
Appendix
References
Abstract
This paper contributes to the existing literature on hedging American options with Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). The study first investigates hyperparameter impact on hedging performance, considering learning rates, training episodes, neural network architectures, training steps, and transaction cost penalty functions. Results highlight the importance of avoiding certain combinations, such as high learning rates with a high number of training episodes or low learning rates with few training episodes and emphasize the significance of utilizing moderate values for optimal outcomes. Additionally, the paper warns against excessive training steps to prevent instability and demonstrates the superiority of a quadratic transaction cost penalty function over a linear version. This study then expands upon the work of Pickard et al. (2024), who utilize a Chebyshev interpolation option pricing method to train DRL agents with market-calibrated stochastic volatility models. While the results of Pickard et al. (2024) showed that these DRL agents achieve satisfactory performance on empirical asset paths, this study introduces a novel approach where new agents at weekly intervals to newly calibrated stochastic volatility models. Results show DRL agents re-trained using weekly market data surpass the performance of those trained solely on the sale date. Furthermore, the paper demonstrates that both single-train and weekly-train DRL agents outperform the Black-Scholes Delta method at transaction costs of 1% and 3%. This practical relevance suggests that practitioners can leverage readily available market data to train DRL agents for effective hedging of options in their portfolios.
\
1. Introduction
In the sale of a put option, the seller faces the risk that the underlying asset price will drop, resulting in a payout to the buyer. As such, financial institutions seek a hedging strategy to offset the potential losses from a short put option position. A common option hedging strategy is the development of a Delta-neutral portfolio, which requires a position of Delta shares to be taken in the underlying, where Delta is the first partial derivative of the option price with respect to the underlying (Hull 2012). Delta hedging stems from the Black and Scholes (BS) (1973) option pricing model, which shows that a European option is perfectly replicated with a continuously rebalanced Delta hedge when the underlying asset price process follows a geometric Brownian motion (GBM) with constant volatility. However, financial markets operate in discrete fashion, volatility is ever-changing, and the impact of transaction costs need be considered. Further, many options are not European, such as American options in which there is a potential for early exercise.
\ Given the outlined market frictions, hedging an option position may be modelled as a sequential decision-making process under uncertainty. A method that has achieved success in such decision-making procedures is reinforcement learning (RL), a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI). Specifically, the combination of RL and neural networks (NNs), called deep RL (DRL), has been used to achieve super-human level performance in video games (Mnih et al. 2013), board games (Silver et al. 2014), and robot control (Lillicrap et al. 2015). Recent advances in quantitative finance have seen DRL be leveraged to achieve desirable results in hedging financial options, as described in the review provided Pickard and Lawryshyn (2023). Notably, prior work by (Pickard et al. 2024) showed the proficiency of DRL agents over the BS Delta strategy when hedging short American put options. Specifically, (Pickard et al. 2024) shows the following:
\ (1) When transaction costs are considered, DRL agents outperform the BS Delta and binomial tree hedge strategies when trained and tested on simulated paths from a GBM process
\ (2) When DRL agents are trained using paths from stochastic volatility models calibrated to market data, DRL agents outperform the BS Delta strategy on the realized asset path for the respective underlying.
\ While recent successes in the field of DRL option hedging are encouraging, particularly the results of Pickard et al. (2024), there is a lack of literature pertaining to best practices for financial institutions looking to implement this “black box” approach. For example, while many papers boast encouraging results, there is little discussion given to the selection of DRL model hyperparameters, which can have a large impact on DRL agent performance (Kiran and Ozyildirim 2022). In the field of option hedging, little discussion is given to hyperparameter choices. Of the 17 studies analysed in Pickard and Lawryshyn (2023), only Du et. al (2020), Assa et al. (2021), and Fathi & Hientzsch (2023) conduct some form of hyperparameter analysis. Moreover, the analysed studies from Pickard and Lawryshyn (2023) consider European style options, and it has been reported that slight environmental changes may impact the optimal hyperparameter settings (Henderson et al. (2017), Eimer et al. (2022)). As such, given that Pickard et al. (2024) provides a first DRL model dedicated to hedging American style options, this study will look to shed light on the hyperparameter tuning process, thereby optimizing the results in the process.
\ The first goal of this work is to provide general hyperparameter selection guidance for practitioners wishing to implement DRL hedging. Therefore, the results of this article will not only show what hyperparameter sets are optimal for the American option hedging task, but what combinations should be avoided. This study will first examine how learning rates, NN architectures, and the number of re-balance steps available to the agent in training effect DRL agent performance. Moreover, considering the results in Pickard et al. (2024), the first work to consider training agents for American options, this article will provide clarity on the key training choices such as the reward function to help the agent achieve optimal hedging. Finally, building off of the key result of Pickard et al. (2024), in that agents trained with market calibrated stochastic volatility model data outperform a BS Delta strategy on empirical asset paths, this article will examine the impact of re-training the agent at weekly intervals to newly available option data.
\
2 Deep Reinforcement Learning
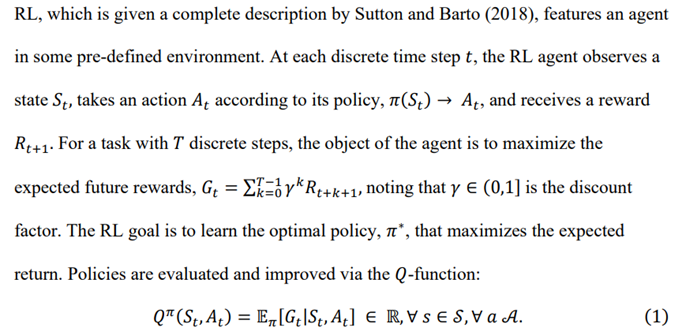
\ 
\ The NN is trained by optimized by minimizing the difference between the output and the target value. This objective function for iteration 𝑖 is given by
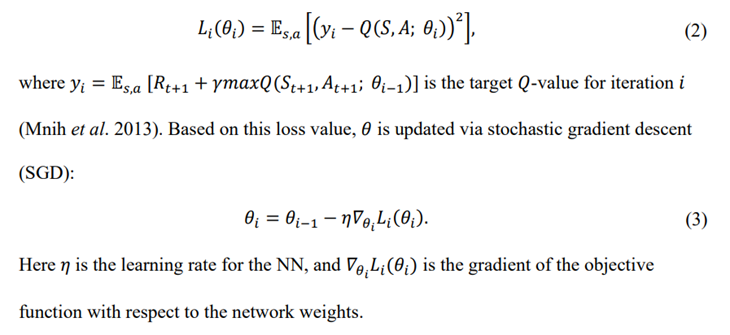
\ 
\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

What John Harbaugh And Mike Tomlin’s Departures Mean For NFL Coaching
Twitter founder's "weekend experiment": Bitchat encryption software becomes a "communication Noah's Ark"

