Bitcoin’s Quantum Countdown Has Already Begun, Warns Veteran Hacker
A cybersecurity veteran turned quantum infrastructure CEO warns that the cryptocurrency industry is dangerously unprepared for the imminent threat of quantum computing to blockchain security.
David Carvalho, CEO of post-quantum infrastructure firm Naoris Protocol and a former ethical hacker since age 13, claims that quantum computers could silently dismantle Bitcoin’s cryptographic foundations within years, not decades.
His warning comes as governments and tech giants already implement “harvest now, decrypt later” strategies, collecting encrypted blockchain data today for future decryption by quantum computers.
Today, approximately 30% of Bitcoin’s circulating supply, roughly 6-7 million BTC, sits vulnerable in older address formats that expose public keys directly to potential quantum attacks.
Understanding the Quantum Threat to Bitcoin’s Core Security
Unlike traditional computers, which process information in binary bits of 0s and 1s, quantum computers utilize quantum bits, or “qubits,” that can exist in multiple states simultaneously through a property called superposition.
This quantum advantage allows these machines to perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers for specific mathematical problems, particularly those involving large number factorization.
Bitcoin’s security relies on elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), specifically the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), which creates a mathematical relationship between public and private keys.
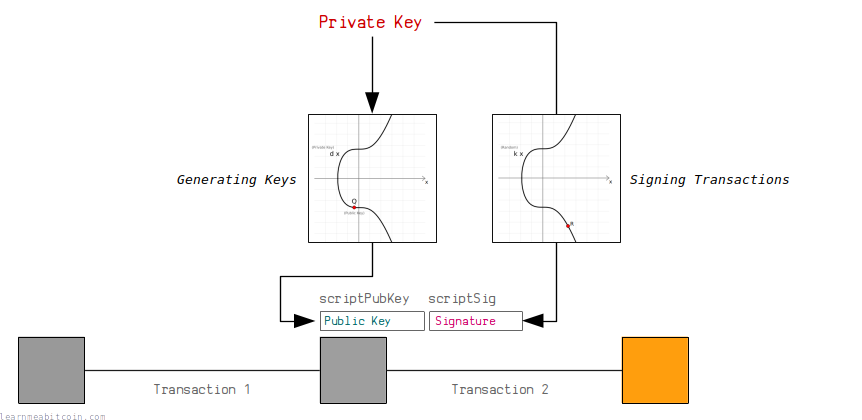 Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm used by Bitcoin (Source: Learn Me A Bitcoin)
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm used by Bitcoin (Source: Learn Me A Bitcoin)
Current computers would require billions of years to reverse-engineer a private key from its corresponding public key due to the computational complexity of solving the discrete logarithm problem underlying ECC.
However, mathematician Peter Shor demonstrated in 1999 that quantum computers could solve these factorization problems exponentially faster using Shor’s algorithm.
This breakthrough would render obsolete the one-way mathematical function that protects Bitcoin wallets, enabling quantum computers to derive private keys from exposed public keys.
Carvalho believes this countdown has already begun because adversaries are systematically collecting encrypted blockchain data under the “harvest now, decrypt later” model.
“The adversaries collecting encrypted blockchain data right now aren’t waiting to attack today,” Carvalho explained, “They’re building data sets for tomorrow.”
Bitcoin addresses fall into different vulnerability categories, with Pay-to-Public-Key (P2PK) formats directly exposing public keys and making them immediate targets for quantum attacks.
Reused Pay-to-Pubkey-Hash (P2PKH) addresses also become vulnerable once their owners move funds, as the transaction reveals the previously hidden public key.
Due to the accelerating development in quantum computing, federal agencies, such as NIST, have warned since 2022 about the urgent need to adopt quantum-resistant algorithms.
Bitcoin users holding funds in older address formats face the highest immediate risk, while node operators and mining infrastructure could become targets for broader network compromise attempts.
Crypto’s Collision Course With Advanced Computing
The quantum threat to Bitcoin reflects a broader technological inflection point where traditional cryptographic assumptions may no longer hold across digital infrastructure.
Major technology companies, including IBM, Google, and Microsoft, are advancing quantum processors with ambitious timelines, with some targeting millions of qubits within this decade.
The joint weapon of quantum computing with artificial intelligence creates, as Carvalho describes, an even more perilous scenario, where AI systems could automatically scan blockchain networks for vulnerabilities while quantum processors compromise cryptographic protections.
Financial institutions are beginning to acknowledge these risks, with companies like BlackRock noting quantum threats in Bitcoin ETF filings and Tether CEO Paolo Ardoino warning about the impact of quantum computing on inactive wallets.
The threat timeline varies among experts, with estimates ranging from 2027 to the mid-2030s for quantum computers capable of breaking Bitcoin’s cryptographic security.
“When the tech catches up, they’ll unlock a decade of secrets in minutes,” Carvalho warned, emphasizing that quantum attacks won’t announce themselves with dramatic computational displays.
The key question remains whether legacy cryptocurrencies can adapt fast enough, or if quantum-resistant blockchains will take the lead in the race to secure digital value.
You May Also Like

Shocking OpenVPP Partnership Claim Draws Urgent Scrutiny

Forward Industries Bets Big on Solana With $4B Capital Plan
