Coding a Fractal Tree With JavaScript and HTML5
\ Fractals, those enigmatic figures that are everywhere but can not be seen by the untrained eye. Today we’ll draw one of the best-known Fractals, using only Vanilla JS and the HTML5 Canvas API. Let’s code!
What You’ll Learn
- What is a Fractal Tree?
- Writing the Fractal Tree in Vanilla JS
- Beyond the Fractal Tree
What is a Fractal Tree?
To define a Fractal Tree, first, we must know the definition of Fractal, of course.
Fractals are never-ending patterns created by repeating mathematical equations, which, on any scale, on any level of zoom, look roughly the same. In other words, a geometric object which’s basic structure, rough or fragmented, repeats itself in different scales.
So if we split a Fractal, we’ll see a reduced-size copy of the whole.
Benoit Mandelbrot, who coined the term Fractal in 1975, said:
\
\ Pretty clear, right?
Here are some examples:
\ 
Now, what is a Fractal Tree?
Imagine a branch, and branches coming out of it, and then two branches coming out of each branch, and so on… that’s what a Fractal Tree looks like.
Its form comes from the Sierpinski triangle (or Sierpinski gasket).
As you can see, one becomes the other when changing the angle between branches:
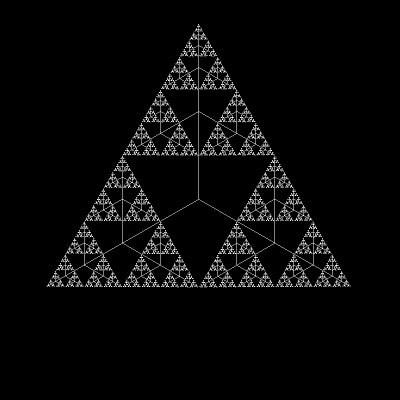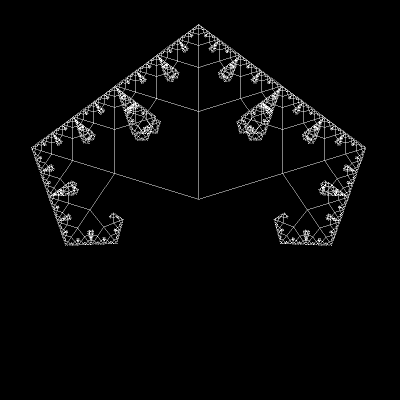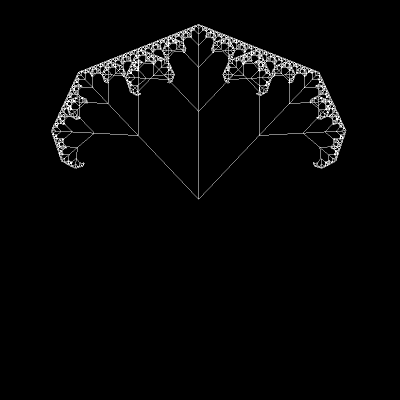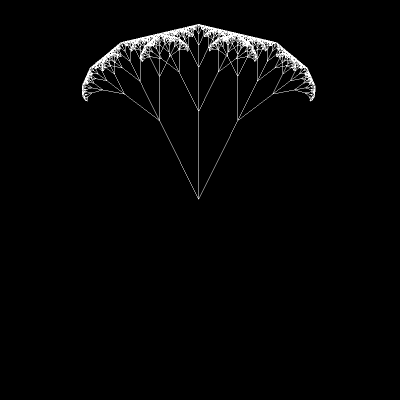
Today, we’ll end up with a figure similar to the final form of that GIF.
Writing the Fractal Tree in Vanilla JS
First of all, here’s the final product (you can tweak it along the way):

Now let’s draw that, step by step.
First of all, we initialize our index.html file with a canvas of any reasonable dimensions and a script tag where all our JS code will be.
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <canvas id="my_canvas" width="1000" height="800"></canvas> <script></script> </body> </html> Then, we start writing our JavaScript.
We initialize our canvas element on JS, by accessing it through the myCanvas variable and creating the 2D rendering context with the ctx (context) variable.
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <canvas id="my_canvas" width="1000" height="800"></canvas> <script> var myCanvas = document.getElementById("my_canvas"); var ctx = myCanvas.getContext("2d"); </script> </body> </html> So yeah, the getContext method adds properties and methods that allow you to draw, in this case, in 2D.
Now it’s time to think. How can we define the algorithm to draw a Fractal tree? Hm… 🤔
Let’s see, we know that the branches keep becoming smaller. And that each branch ends with two branches coming out of it, one to the left and one to the right.
In other words, when a branch is long enough, attach two smaller branches to it. Repeat.
It kinda sounds like we should use some recursive statement somewhere, isn’t it?
Back to the code, we now define our function fractalTree that should take at least four arguments: the X and Y coordinates where the branch starts, the length of its branch, and its angle.
Inside our function, we begin the drawing with the beginPath() method, and then save the state of the canvas with the save() method.
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <canvas id="my_canvas" width="1000" height="800"></canvas> <script> var myCanvas = document.getElementById("my_canvas"); var ctx = myCanvas.getContext("2d"); function draw(startX, startY, len, angle) { ctx.beginPath(); ctx.save(); } </script> </body> </html> The beginPath method is often used when you start a new line or figure that has a fixed style, like the same color along the entire line, or the same width. The save method just saves the entire state of the canvas by pushing the current state onto a stack.
Now we’ll draw our Fractal Tree by drawing a line (branch), rotating the canvas, drawing the next branch, and so on. It goes like this (I’ll explain each method below the code sample):
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <canvas id="my_canvas" width="1000" height="800"></canvas> <script> var myCanvas = document.getElementById("my_canvas"); var ctx = myCanvas.getContext("2d"); function draw(startX, startY, len, angle) { ctx.beginPath(); ctx.save(); ctx.translate(startX, startY); ctx.rotate(angle * Math.PI/180); ctx.moveTo(0, 0); ctx.lineTo(0, -len); ctx.stroke(); if(len < 10) { ctx.restore(); return; } draw(0, -len, len*0.8, -15); draw(0, -len, len*0.8, +15); ctx.restore(); } draw(400, 600, 120, 0) </script> </body> </html> So we first add three methods, translate, rotate, and moveTo, which “moves” the canvas, its origin, and our “pencil” so we can draw the branch in our desired angle. It’s like we are drawing a branch, then centering this branch (by moving the whole canvas), and then drawing a new branch from the end of our previous branch.
The last two methods before the if statement are lineTo and stroke; the first adds a straight line to the current path, and the second one renders it. You can think of it like this: lineTo gives the order, and stroke executes it.
Now we have an if statement that tells when to stop the recursion, when to stop drawing. The restore method, as stated in the MDN Docs, “restores the most recently saved canvas state by popping the top entry in the drawing state stack”.
After the if statement, we have the recursive call and another call to the restore method. And then a call to the function that we just finished.
Now run the code in your browser. You’ll see, finally, a Fractal Tree!
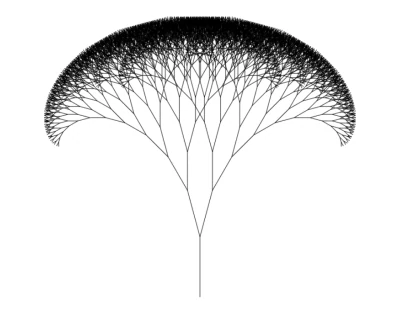
Awesome, right? Now let’s make it even better.
We’ll add a new parameter to our draw function, branchWidth, to make our Fractal Tree more realistic.
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <canvas id="my_canvas" width="1000" height="800"></canvas> <script> var myCanvas = document.getElementById("my_canvas"); var ctx = myCanvas.getContext("2d"); function draw(startX, startY, len, angle, branchWidth) { ctx.lineWidth = branchWidth; ctx.beginPath(); ctx.save(); ctx.translate(startX, startY); ctx.rotate(angle * Math.PI/180); ctx.moveTo(0, 0); ctx.lineTo(0, -len); ctx.stroke(); if(len < 10) { ctx.restore(); return; } draw(0, -len, len*0.8, angle-15, branchWidth*0.8); draw(0, -len, len*0.8, angle+15, branchWidth*0.8); ctx.restore(); } draw(400, 600, 120, 0, 10) </script> </body> </html> So in every iteration, we are making each branch thinner. I’ve also changed the angle parameter in the recursive call to make a more “open” tree.
Now, let’s add some color! And shadows, why not.
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <canvas id="my_canvas" width="1000" height="800"></canvas> <script> var myCanvas = document.getElementById("my_canvas"); var ctx = myCanvas.getContext("2d"); function draw(startX, startY, len, angle, branchWidth) { ctx.lineWidth = branchWidth; ctx.beginPath(); ctx.save(); ctx.strokeStyle = "green"; ctx.fillStyle = "green"; ctx.translate(startX, startY); ctx.rotate(angle * Math.PI/180); ctx.moveTo(0, 0); ctx.lineTo(0, -len); ctx.stroke(); ctx.shadowBlur = 15; ctx.shadowColor = "rgba(0,0,0,0.8)"; if(len < 10) { ctx.restore(); return; } draw(0, -len, len*0.8, angle-15, branchWidth*0.8); draw(0, -len, len*0.8, angle+15, branchWidth*0.8); ctx.restore(); } draw(400, 600, 120, 0, 10) </script> </body> </html> Both color methods are self-explanatory (strokeStyle and fillStyle). Also, the shadow ones, shadowBlur and shadowColor.
And that’s it! Save the file and open it with your browser to see the final product.
Now I encourage you to play with the code! Change the shadowColor, the fillStyle, make a shorter or longer Fractal Tree, change the angle, or try to add leaves, that should be challenging 😉
Beyond the Fractal Tree
As I showed you at the beginning of this post, there are different Fractals. Ain’t gonna be easy to make all those with the Canvas API, but it should be possible. I made some of those in the C programming language, and I’ve also played around with p5.js.
p5.js is an Open Source JavaScript library made by artists, for artists, based on the Processing language. You can draw or animate anything imaginable. If you are interested in making art with code, it’s a must. They have a great get-started page that you can check out here.
Well, that’s it for now! Thanks for reading, comment any questions, and see you in my next post!
\
You May Also Like

Wilma now a low-pressure area, to drench Palawan, Western Visayas

Best Crypto to Buy as Saylor & Crypto Execs Meet in US Treasury Council
