How WormHole Speeds Up Pathfinding in Billion-Edge Graphs
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Our Contribution
1.2 Setting
1.3 The algorithm
-
Related Work
-
Algorithm
3.1 The Structural Decomposition Phase
3.2 The Routing Phase
3.3 Variants of WormHole
-
Theoretical Analysis
4.1 Preliminaries
4.2 Sublinearity of Inner Ring
4.3 Approximation Error
4.4 Query Complexity
-
Experimental Results
5.1 WormHole𝐸, WormHole𝐻 and BiBFS
5.2 Comparison with index-based methods
5.3 WormHole as a primitive: WormHole𝑀
References
1.1 Our Contribution
We design a new algorithm, WormHole, that creates a data structure allowing us to answer multiple shortest path inquiries by exploiting the typical structure of many social and information networks. WormHole is simple, easy to implement, and theoretically backed. We provide several variants of it, each suitable for a different setting, showing excellent empirical results on a variety of network datasets. Below are some of its key features:
\ • Performance-accuracy tradeoff. To the best of our knowledge, ours is the first approximate sublinear shortest paths algorithm in large networks. The fact that we allow small additive error, gives rise to a trade-off between preprocessing time/space and per-inquiry time, and allows us to come
\ 
\ up with a solution with efficient preprocessing and fast perinquiry time. Notably, our most accurate (but slowest) variant, WormHole𝐸, has near-perfect accuracy: more than 90% of the inquiries are answered with no additive error, and in all networks, more than 99% of the inquiries are answered with additive error at most 2. See Table 3 for more details.
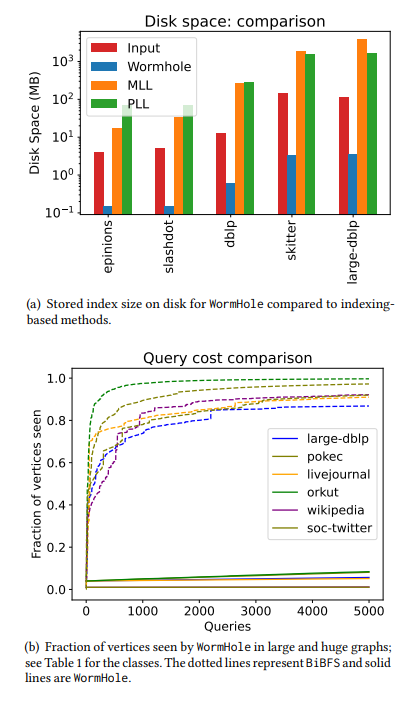
\ • Extremely rapid setup time. Our longest index construction time was just two minutes even for billion-edged graphs. For context, PLL and MLL timed out on half of the networks that we tested, and for moderately sized graphs where PLL and MLL did finish their runs, WormHole index construction was×100 faster. Namely, WormHole finished in seconds while PLL took hours. See Table 4 and Table 5. This rapid setup time is achieved due to the use of a sublinearly-sized index. For the largest networks we considered, it is sufficient to take an index of about 1% of the nodes to get small mean additive error – see Table 1. For smaller networks, it may be up to 6%.
\ • Fast inquiry time. Compared to BiBFS, the vanilla version WormHole𝐸 (without any index-based optimizations) is ×2 faster for almost all graphs and more than ×4 faster on the three largest graphs that we tested. A simple variant WormHole𝐻 achieves an order of magnitude improvement at some cost to accuracy: consistently 20× faster across almost all graphs, and more than 180× for the largest graph we have. See Table 3 for a full comparison. Indexing based methods typically answer inquiries in microseconds; both of the aforementioned variants are still in the millisecond regime.
\ • Combining WormHole and the state of the art. WormHole works by storing a small subset of vertices on which we compute the exact shortest paths. For arbitrary inquiries, we route our path through this subset, which we call the core. We use this insight to provide a third variant, WormHole𝑀 by implementing the state of the art for shortest paths, MLL, on the core. This achieves inquiry times that are comparable to MLL (with the same accuracy guarantee as WormHole𝐻 ) at a fraction of the setup cost, and runs for massive graphs where MLL does not terminate. We explore this combined approach in §5.3, and provide statistics in Table 6.
\ • Sublinear query complexity. The query complexity refers to the number of vertices queried by the algorithm. In a limited query access model where querying a node reveals its list of neighbors(see §1.2), the query complexity of our algorithm scales very well with the number of distance / shortest path inquiries made. To answer 5000 approximate shortest path inquiries, our algorithm only observes between 1% and 20% of the nodes for most networks. In comparison, BiBFS sees more than 90%of the graph to answer a few hundred shortest path inquiries. See Figure 2 and Figure 5 for a comparison.
\ • Provable guarantees on error and performance. In §4 we prove a suite of theoretical results complementing and explaining the empirical performance. The results, stated informally below, are proved for the Chung-Lu model of random graphs with a power-law degree distribution [15–17].
\ Theorem 1.1 (Informal). In a Chung-Lu random graph𝐺 with power-law exponent 𝛽 ∈ (2,3) on 𝑛 vertices, WormHole has the following guarantees with high probability:
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Talya Eden, Bar-Ilan University ([email protected]);
(2) Omri Ben-Eliezer, MIT ([email protected]);
(3) C. Seshadhri, UC Santa Cruz ([email protected]).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::
\
You May Also Like
Ethereum Price Prediction: ETH Targets $10,000 In 2026 But Layer Brett Could Reach $1 From $0.0058

UK and US Seal $42 Billion Tech Pact Driving AI and Energy Future
