Network Size and Task Number: Ablation Study on IIL Performance and Stability
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Related works
-
Problem setting
-
Methodology
4.1. Decision boundary-aware distillation
4.2. Knowledge consolidation
-
Experimental results and 5.1. Experiment Setup
5.2. Comparison with SOTA methods
5.3. Ablation study
-
Conclusion and future work and References
\
Supplementary Material
- Details of the theoretical analysis on KCEMA mechanism in IIL
- Algorithm overview
- Dataset details
- Implementation details
- Visualization of dusted input images
- More experimental results
12. More experimental results
12.1. Ablation study on network size
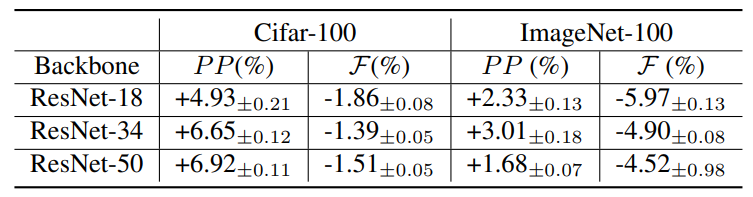
\ To investigate the impact of network size on the proposed method, we compare the performance of ResNet-18, ResNet-34 and ResNet-50 on the ImageNet-100. As shown in Tab. 5, the proposed method performs well with bigger
\ 
\ 
\ network size. When the network size is larger, more parameters can be utilized for new knowledge learning with the proposed decision boundary-aware distillation. Hence, consolidating knowledge from student to teacher causes less forgetting.
\ 12.2. Ablation study on the task number
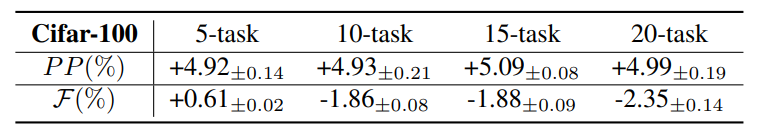
\ As mentioned in Sec. 7, our method accumulates the error along with the consecutive IIL tasks. However, such a kind of error accumulates slowly and mainly affects the performance on old tasks, i.e. forgetting rate. We further study the impact of task length on the performance of the proposed method by splitting the incremental data into different number of subsets. As shown in Tab. 6, with the incremental of task number, the performance promotion changes less but the forgetting rate increased slightly. Minor variation of performance promotion reveals that the proposed method is stable in learning new knowledge, irrespective of the number of tasks. The acquisition of new knowledge primarily hinges on the volume of new data involved. Although we increase the task number in the experiments, the total number of new data utilized in IIL phase is the same. While increasing the task number will increase the EMA steps, which causes more forgetting on the old data. Experimental results in Tab. 6 well validate our analysis in Sec. 7.
\ Compared to the performance promotion, forgetting on the old data is negligible. Noteworthy, when the task number is relatively small, such as 5 in Tab. 6, the proposed method slightly boosts the model’s performance on the base data. This behavior is similar with full-data model, which demonstrates the capability of our method in accumulating knowledge from new data.
\ 12.3. Detailed comparison between the KC-EMA and vanilla EMA
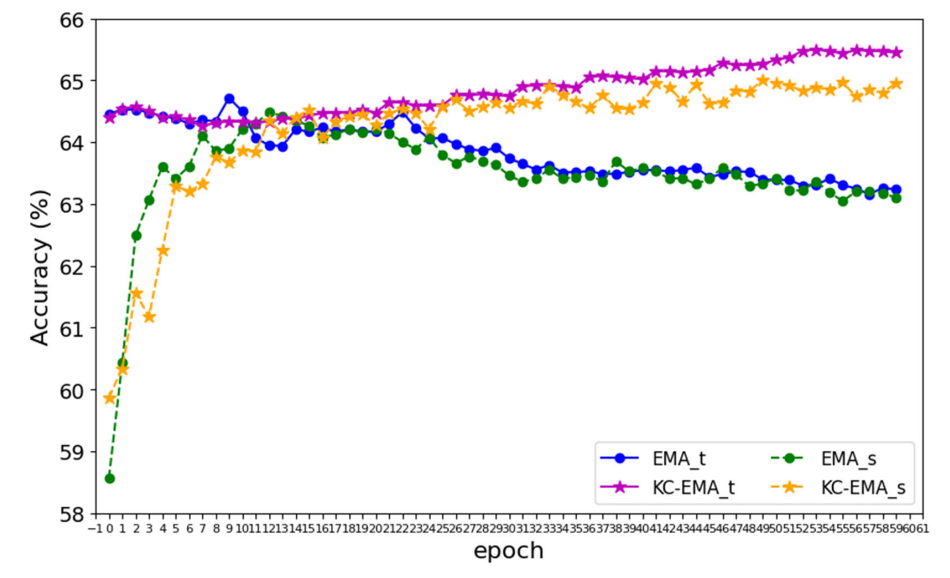
\ The performance of vanilla EMA and the proposed KCEMA during training is shown in Fig. 11. As can be seen, the student model’s accuracy initially plummets due to the introduction of new data. However, around the 10th epoch,
\ 
\ there’s a resurgence in accuracy for both the KC-EMA and vanilla EMA models. Therefore, we empirically set a freezing epoch of 10 in the proposed method.
\ When EMA is applied post the 10th epoch, the teacher model in the vanilla EMA is rapidly drawn towards the student model. This homogenization, however, doesn’t enhance either model. Instead, it leads to a decline in test accuracy due to overfitting to the new data. In contrast, with KC-EMA, both the teacher and student models exhibit gradual growth,, which indicates a knowledge accumulation in these two models. On one hand, consolidating new knowledge to the teacher model improves its test performance. On the other hand, a teacher model equipped with new knowledge liberates the student model to learn new data. That is, constraints from the teacher in distillation is alleviated.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Qiang Nie, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou);
(2) Weifu Fu, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(3) Yuhuan Lin, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(4) Jialin Li, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(5) Yifeng Zhou, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(6) Yong Liu, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(7) Qiang Nie, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou);
(8) Chengjie Wang, Tencent Youtu Lab.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like
Ethereum Price Prediction: ETH Targets $10,000 In 2026 But Layer Brett Could Reach $1 From $0.0058

UK and US Seal $42 Billion Tech Pact Driving AI and Energy Future
