Why Gradient Descent Converges (and Sometimes Doesn’t) in Neural Networks
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1. Introductory remarks
1.2. Basics of neural networks
1.3. About the entropy of direct PINN methods
1.4. Organization of the paper
-
Non-diffusive neural network solver for one dimensional scalar HCLs
2.1. One shock wave
2.2. Arbitrary number of shock waves
2.3. Shock wave generation
2.4. Shock wave interaction
2.5. Non-diffusive neural network solver for one dimensional systems of CLs
2.6. Efficient initial wave decomposition
-
Gradient descent algorithm and efficient implementation
3.1. Classical gradient descent algorithm for HCLs
3.2. Gradient descent and domain decomposition methods
-
Numerics
4.1. Practical implementations
4.2. Basic tests and convergence for 1 and 2 shock wave problems
4.3. Shock wave generation
4.4. Shock-Shock interaction
4.5. Entropy solution
4.6. Domain decomposition
4.7. Nonlinear systems
-
Conclusion and References
3. Gradient descent algorithm and efficient implementation
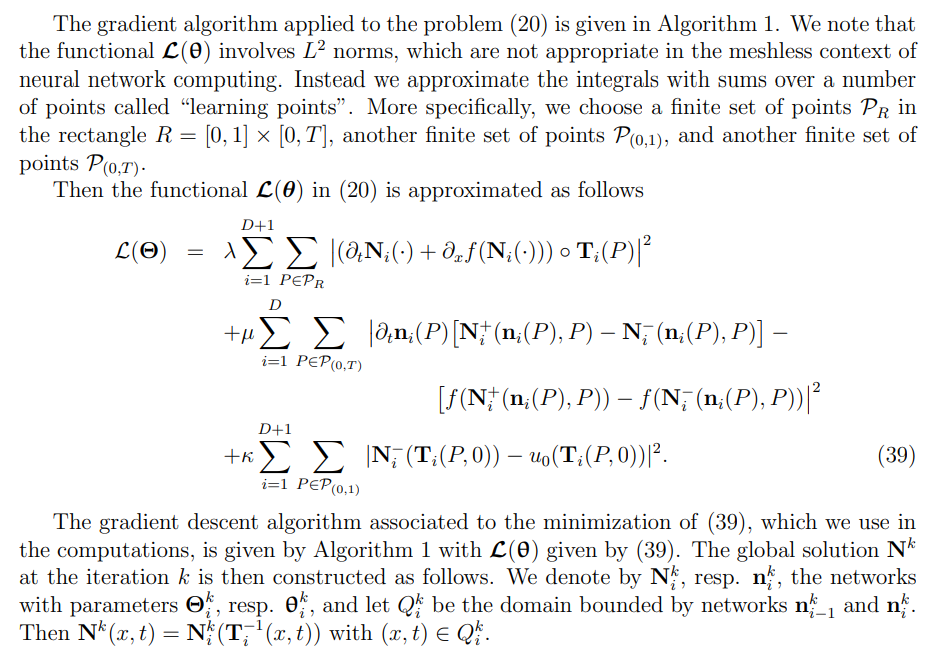
In this section we discuss the implementation of gradient descent algorithms for solving the minimization problems (11), (20) and (35). We note that these problems involve a global loss functional measuring the residue of HCL in the whole domain, as well Rankine-Hugoniot conditions, which results in training of a number of neural networks. In all the tests we have done, the gradient descent method converges and provides accurate results. We note also, that in problems with a large number of DLs, the global loss functional couples a large number of networks and the gradient descent algorithm may converge slowly. For these problems we present a domain decomposition method (DDM).
3.1. Classical gradient descent algorithm for HCLs
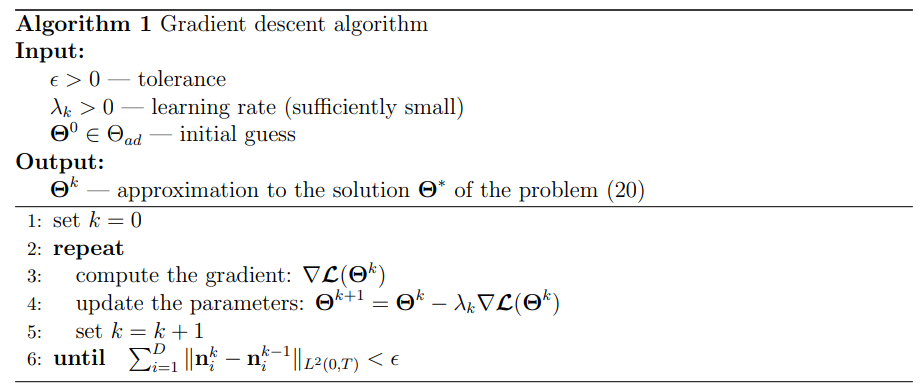
All the problems (11), (20) and (35) being similar, we will demonstrate in details the algorithm for the problem (20). We assume that the solution is initially constituted by i) D ∈ {1, 2, . . . , } entropic shock waves emanating from x1, . . . , xD, ii) an arbitrary number of rarefaction waves, and that iii) there is no shock generation for t ∈ [0, T].
\ 
\ 
3.2. Gradient descent and domain decomposition methods
Rather than minimizing the global loss function (21) (or (12), (36)), we here propose to decouple the optimization of the neural networks, and make it scalable. The approach is closely connected to domain decomposition methods (DDMs) Schwarz Waveform Relaxation (SWR) methods [21, 22, 23]. The resulting algorithm allows for embarrassingly parallel computation of minimization of local loss functions.
\ \ 
\ \ \ 
\ \ \ 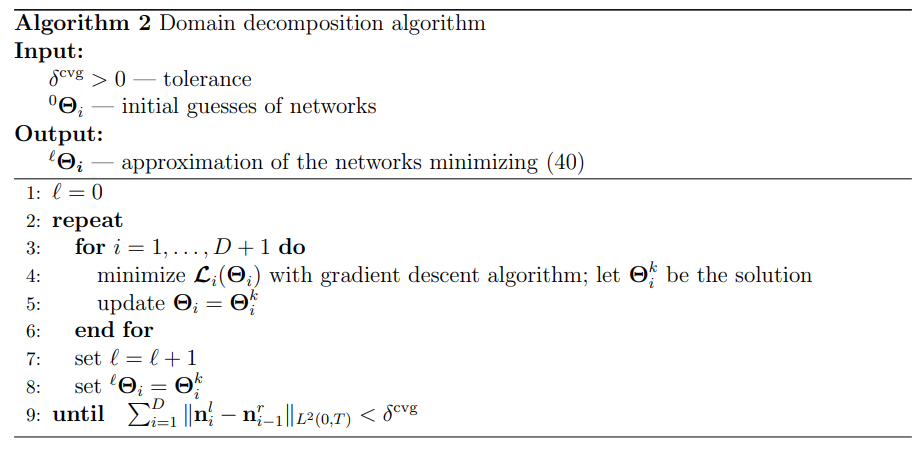
\ \ In conclusion, the DDM becomes relevant thanks to its scalability and for kDDMkLocal < kGlobal, which is expected for D large.
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Emmanuel LORIN, School of Mathematics and Statistics, Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada, K1S 5B6 and Centre de Recherches Mathematiques, Universit´e de Montr´eal, Montreal, Canada, H3T 1J4 ([email protected]);
(2) Arian NOVRUZI, a Corresponding Author from Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON K1N 6N5, Canada ([email protected]).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Wilma now a low-pressure area, to drench Palawan, Western Visayas

The Future of Secure Messaging: Why Decentralization Matters
