Why Researchers Are Betting on PCs to Power the Next Wave of AI
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Preliminaries and Related Work
-
Key Bottlenecks in PC Parallelization
-
Harnessing Block-Based PC Parallelization
4.1. Fully Connected Sum Layers
4.2. Generalizing To Practical Sum Layers
4.3. Efficient Implementations by Compiling PC Layers
4.4. Analysis: IO and Computation Overhead
-
Optimizing Backpropagation with PC Flows
-
Experiments
6.1. Faster Models with PyJuice
6.2. Better PCs At Scale
6.3. Benchmarking Existing PCs
-
Conclusion, Acknowledgements, Impact Statement, and References
A. Algorithm Details
B. Additional Technical Details
C. Experimental Details
D. Additional Experiments
\
2. Preliminaries and Related Work
Many probabilistic inference tasks can be cast into computing sums of products. By viewing them from a computation graph standpoint, PCs provide a unified perspective on many bespoke representations of tractable probability distributions, including Arithmetic Circuits (Darwiche, 2002; 2003), Sum-Product Networks (Poon & Domingos, 2011), Cutset Networks (Rahman et al., 2014), and Hidden Markov Models (Rabiner & Juang, 1986). Specifically, PCs define distributions with computation graphs consisting of sum and product operations, as elaborated below.
\ 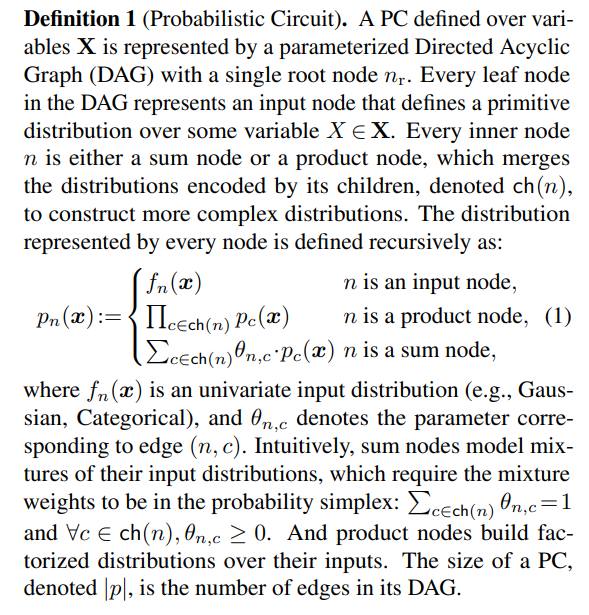
\ The key to guaranteeing exact and efficient computation of various probabilistic queries is to impose proper structural constraints on the DAG of the PC. As an example, with smoothness and decomposability (Poon & Domingos, 2011), computing any marginal probability amounts to a forward pass (children before parents) following Equation (1), with the only exception that we set the value of input nodes defined on marginalized variables to be 1. Please refer to Choi et al. (2020) for a comprehensive overview of different structural constraints and what queries they enable.
\ 
\ For example, Peharz et al. (2020a) demonstrate how the above parameter gradients can be used to apply ExpectationMaximization (EM) updates, and Vergari et al. (2021) elaborates how the forward pass can be used to compute various probabilistic and information-theoretic queries when coupled with PC structure transformation algorithms. Therefore, the speed and memory efficiency of these two procedures largely determine the overall efficiency of PCs.
\ 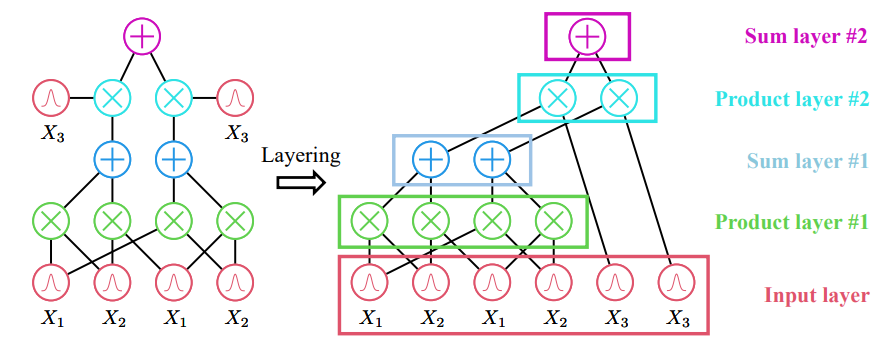
\ Related work on accelerating PCs. There has been a great amount of effort put into speeding up training and inference for PCs. One of the initial attempts performs nodebased computations on both CPUs (Lowd & Rooshenas, 2015) and GPUs (Pronobis et al., 2017; Molina et al., 2019), i.e., by computing the outputs for a mini-batch of inputs (data) recursively for every node. Despite its simplicity, it fails to fully exploit the parallel computation capability possessed by modern GPUs since it can only parallelize over a batch of samples. This problem is mitigated by also parallelizing topologically independent nodes (Peharz et al., 2020a; Dang et al., 2021). Specifically, a PC is chunked into topological layers, where nodes in the same layer can be computed in parallel. This leads to 1-2 orders of magnitude speedup compared to node-based computation.
\ The regularity of edge connection patterns is another key factor influencing the design choices. Specifically, EiNets (Peharz et al., 2020a) leverage off-the-shelf Einsum operations to parallelize dense PCs where every layer contains groups of densely connected sum and product/input nodes. Mari et al. (2023) generalize the notion of dense PCs to tensorized PCs, which greatly expands the scope of EiNets. Dang et al. (2021) instead focus on speeding up sparse PCs, where different nodes could have drastically different numbers of edges. They use custom CUDA kernels to balance the workload of different GPU threads and achieve decent speedup on both sparse and dense PCs.
\ Another thread of work focuses on designing computation hardware that is more suitable for PCs. Specifically, Shah et al. (2021) propose DAG Processing Units (DPUs) that can efficiently traverse sparse PCs, Dadu et al. (2019) introduce an indirect read reorder-buffer to improve the efficiency of data-dependent memory accesses in PCs, and Yao et al. (2023) use addition-as-int multiplications to significantly improve the energy efficiency of PC inference algorithms.
\ 
\ Applications of PCs. PCs have been applied to many domains such as explainability and causality (Correia et al., 2020; Wang & Kwiatkowska, 2023), graph link prediction (Loconte et al., 2023), lossless data compression (Liu et al., 2022), neuro-symbolic AI (Xu et al., 2018; Manhaeve et al., 2018; Ahmed et al., 2022a;b), gradient estimation (Ahmed et al., 2023b), graph neural networks rewiring (Qian et al., 2023), and even large language model detoxification (Ahmed et al., 2023a).
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Anji Liu, Department of Computer Science, University of California, Los Angeles, USA ([email protected]);
(2) Kareem Ahmed, Department of Computer Science, University of California, Los Angeles, USA;
(3) Guy Van den Broeck, Department of Computer Science, University of California, Los Angeles, USA;
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

BitGo expands its presence in Europe

Wormhole Unveils W Token 2.0 with Enhanced Tokenomics

