僅使用 0.2% 的參數擊敗完全微調
連結表
摘要和1. 引言
-
背景
2.1 專家混合
2.2 適配器
-
適配混合
3.1 路由策略
3.2 一致性正則化
3.3 適配模組合併和3.4 適配模組共享
3.5 與貝葉斯神經網絡和模型集成的連接
-
實驗
4.1 實驗設置
4.2 主要結果
4.3 消融研究
-
相關工作
-
結論
-
局限性
-
致謝和參考文獻
附錄
A. 少樣本NLU數據集 B. 消融研究 C. NLU任務的詳細結果 D. 超參數
5 相關工作
預訓練語言模型的參數高效微調。 最近關於參數高效微調(PEFT)的工作大致可分為兩類
\ 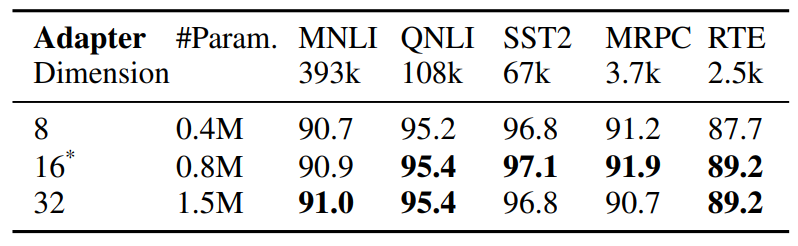
\ 類別:(1)調整現有參數的子集,包括頭部微調(Lee等,2019)、偏置項調整(Zaken等,2021),(2)調整新引入的參數,包括適配器(Houlsby等,2019;Pfeiffer等,2020)、提示調整(Lester等,2021)、前綴調整(Li和Liang,2021)和低秩適配(Hu等,2021)。與之前在單一適配模組上操作的工作不同,AdaMix引入了適配模組混合,在訓練期間使用隨機路由,並在推理期間合併適配模組,以保持與單一模組相同的計算成本。此外,AdaMix可以應用於任何PEFT方法之上,進一步提升其性能。
\ 專家混合(MoE)。 Shazeer等,2017引入了MoE模型,該模型具有單一閘控網絡,採用Top-k路由和專家間的負載平衡。Fedus等,2021提出了Top-1路由的初始化和訓練方案。Zuo等,2021提出了隨機路由的一致性正則化;Yang等,2021提出了帶有專家原型的kTop-1路由,而Roller等,2021;Lewis等,2021解決了其他負載平衡問題。上述所有工作都研究了從頭開始預訓練整個模型的稀疏MoE。相比之下,我們研究通過僅調整非常少量的稀疏適配器參數來實現預訓練語言模型的參數高效適配。
\ 平均模型權重。 最近的探索(Szegedy等,2016;Matena和Raffel,2021;Wortsman等,2022;Izmailov等,2018)研究了通過平均所有模型權重進行模型聚合。(Matena和Raffel,2021)提出合併在各種文本分類任務上微調的預訓練語言模型。(Wortsman等,2022)探索了在相同任務上使用不同超參數配置的各種獨立運行的模型權重平均。與上述關於完整模型微調的工作不同,我們專注於參數高效微調。我們探索權重平均用於合併適配模組的權重,這些模組由在模型調整期間更新的小型可調參數組成,同時保持大型模型參數不變。
6 結論
我們開發了一個新的框架AdaMix,用於大型預訓練語言模型(PLM)的參數高效微調(PEFT)。AdaMix利用適配模組混合來提高下游任務性能,而不增加底層適配方法的計算成本(例如,FLOPs,參數)。我們展示了AdaMix可以與不同的PEFT方法(如適配器和低秩分解)一起工作並改進它們,跨越NLU和NLG任務。
\ 通過僅調整PLM參數的0.1-0.2%,AdaMix優於更新所有模型參數的完整模型微調以及其他最先進的PEFT方法。
7 局限性
提出的AdaMix方法在某種程度上計算密集,因為它涉及大規模語言模型的微調。提出的AdaMix的訓練成本高於標準PEFT方法,因為訓練過程涉及多個適配器副本。根據我們的經驗觀察,AdaMix的訓練迭代次數通常是標準PEFT方法訓練的1~2倍。這對訓練所描述模型的碳足跡產生了負面影響。
\ AdaMix與大多數現有的參數高效微調(PEFT)研究正交,並且能夠潛在地提高任何PEFT方法的性能。在這項工作中,我們探索了兩種代表性PEFT方法,如適配器和LoRA,但我們沒有嘗試其他組合,如提示調整和前綴調整。我們將這些研究留給未來的工作。
8 致謝
作者感謝匿名審稿人的寶貴意見和有益建議,並感謝Guoqing Zheng和Ruya Kang對項目的深刻見解。這項工作部分由美國國家科學基金會資助,資助號為NSFIIS 1747614和NSF-IIS-2141037。本材料中表達的任何意見、發現和結論或建議均為作者的觀點,不一定反映國家科學基金會的觀點。
參考文獻
Armen Aghajanyan, Sonal Gupta, and Luke Zettlemoyer. 2021. Intrinsic dimensionality explains the effectiveness of language model fine-tuning. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 7319– 7328, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics.
\ Roy Bar Haim, Ido Dagan, Bill Dolan, Lisa Ferro, Danilo Giampiccolo, Bernardo Magnini, and Idan Szpektor. 2006. The second PASCAL recognising textual entailment challenge.
\ Luisa Bentivogli, Peter Clark, Ido Dagan, and Danilo Giampiccolo. 2009. The fifth PASCAL recognizing textual entailment challenge. In TAC.
\ Tom Brown, Benjamin Mann, Nick Ryder, Melanie Subbiah, Jared D Kaplan, Prafulla Dhariwal, Arvind Neelakantan, Pranav Shyam, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Sandhini Agarwal, Ariel HerbertVoss, Gretchen Krueger, Tom Henighan, Rewon Child, Aditya Ramesh, Daniel Ziegler, Jeffrey Wu, Clemens Winter, Chris Hesse, Mark Chen, Eric Sigler, Mateusz Litwin, Scott Gray, Benjamin Chess, Jack Clark, Christopher Berner, Sam McCandlish, Alec Radford, Ilya Sutskever, and Dario Amodei. 2020. Language models are few-shot learners. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 33, pages 1877–1901. Curran Associates, Inc.
\ Ido Dagan, Oren Glickman, and Bernardo Magnini. 2005. The PASCAL recognising textual entailment challenge. In the First International Conference on Machine Learning Challenges: Evaluating Predictive Uncertainty Visual Object Classification, and Recognizing Textual Entailment.
\ Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee, and Kristina Toutanova. 2019. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL-HLT 2019, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pages 4171–4186.
\ William Fedus, Barret Zoph, and Noam Shazeer. 2021. Switch transformers: Scaling to trillion parameter models with simple and efficient sparsity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.03961.
\ Jonathan Frankle, Gintare Karolina Dziugaite, Daniel Roy, and Michael Carbin. 2020. Linear mode connectivity and the lottery ticket hypothesis. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 3259–3269. PMLR.
\ Yarin Gal and Zoubin Ghahramani. 2015. Dropout as a bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. CoRR, abs/1506.02142.
\ Yarin Gal, Riashat Islam, and Zoubin Ghahramani. 2017. Deep Bayesian active learning with image data. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, volume 70 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pages 1183–1192. PMLR.
\ Tianyu Gao, Adam Fisch, and Danqi Chen. 2021. Making pre-trained language models better few-shot learners. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL).
\ Claire Gardent, Anastasia Shimorina, Shashi Narayan, and Laura Perez-Beltrachini. 2017. The webnlg challenge: Generating text from rdf data. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Natural Language Generation, pages 124–133.
\ Danilo Giampiccolo, Bernardo Magnini, Ido Dagan, and Bill Dolan. 2007. The third PASCAL recognizing textual entailment challenge. In the ACLPASCAL Workshop on Textual Entailment and Paraphrasing.
\ Neil Houlsby, Andrei Giurgiu, Stanislaw Jastrzebski, Bruna Morrone, Quentin De Laroussilhe, Andrea Gesmundo, Mona Attariyan, and Sylvain Gelly. 2019. Parameter-efficient transfer learning for nlp. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 2790–2799. PMLR.
\ Edward J Hu, Yelong Shen, Phillip Wallis, Zeyuan Allen-Zhu, Yuanzhi Li, Shean Wang, Lu Wang, and Weizhu Chen. 2021. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09685.
\ Pavel Izmailov, Dmitrii Podoprikhin, Timur Garipov, Dmitry Vetrov, and Andrew Gordon Wilson. 2018. Averaging weights leads to wider optima and better generalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.05407.
\ Jaejun Lee, Raphael Tang, and Jimmy Lin. 2019. What would elsa do? freezing layers during transformer fine-tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.03090.
\ Dmitry Lepikhin, HyoukJoong Lee, Yuanzhong Xu, Dehao Chen, Orhan Firat, Yanping Huang, Maxim Krikun, Noam Shazeer, and Zhifeng Chen. 2020. Gshard: Scaling giant models with conditional computation and automatic sharding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.16668.
\ Brian Lester, Rami Al-Rfou, and Noah Constant. 2021. The power of scale for parameter-efficient prompt tuning. CoRR, abs/2104.08691.
\ Mike Lewis, Shruti Bhosale, Tim Dettmers, Naman Goyal, and Luke Zettlemoyer. 2021. Base layers: Simplifying training of large, sparse models. In ICML.
\ Xiang Lisa Li and Percy Liang. 2021. Prefixtuning: Optimizing continuous prompts for generation. CoRR, abs/2101.00190.
\ Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, and Veselin Stoyanov. 2019. Roberta: A robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach. CoRR, abs/1907.11692.
\ Yuning Mao, Lambert Mathias, Rui Hou, Amjad Almahairi, Hao Ma, Jiawei Han, Wen-tau Yih, and Madian Khabsa. 2021. Unipelt: A unified framework for parameter-efficient language model tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.07577.
\ Michael Matena and Colin Raffel. 2
您可能也會喜歡

策略如何在比特幣持有量疑慮中保持 Nasdaq 100 現貨強勢

Ripple 獲得美國銀行業准入,推動 XRP 長期目標邁向 $27
