Hackers Exploit Ethereum to Inject Malware in Popular Coding Libraries
Hackers are now exploiting vulnerabilities in widely-used NPM coding libraries to inject malware into Ethereum smart contracts, according to cybersecurity research by blockchain compliance firm Reversing Labs(RL).
In a September 3 blog post detailing the discovery, researcher Lucija Valentić revealed that threat actors bypass security scans by exploiting new open-source malware present in the Node Package Manager (NPM) package repository, which contains extensive JavaScript packages and libraries.
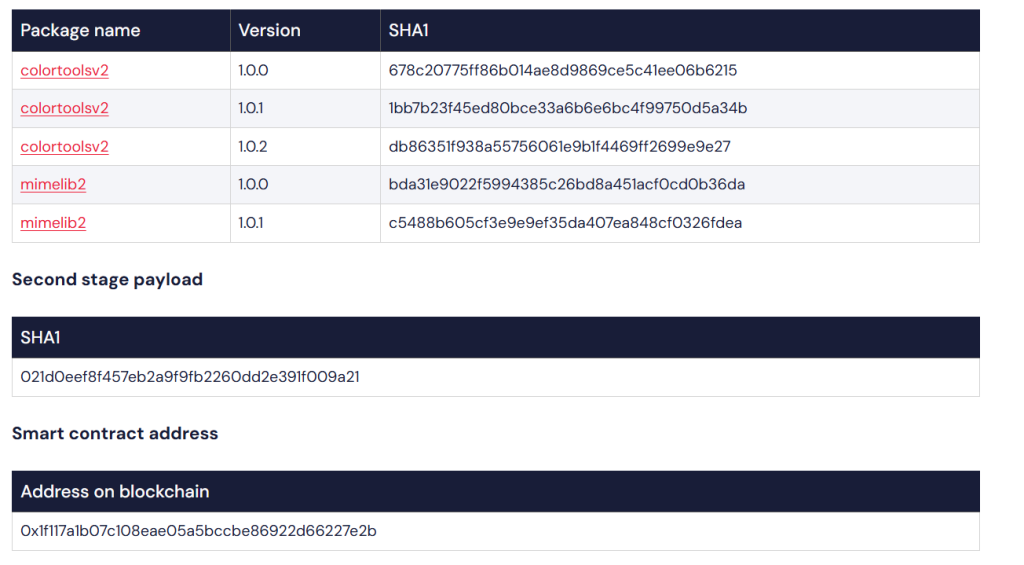
The most destructive malware discovered was “colortoolsv2” and “mimelib2“, both published in July, which were found to abuse smart contracts to conceal malicious commands that install downloader malware on infected systems.
 Source: ReversingLabs
Source: ReversingLabs
How Ethereum Smart Contracts Turn Into Malware Command Centers
These packages are part of broader open-source libraries affecting both NPM and GitHub, where malicious supply chain actors use advanced social engineering and deception tactics to trick developers into incorporating harmful code into their projects.
According to ReversingLabs, 2025 has witnessed a diverse range of malicious campaigns targeting NPM, the leading online repository for JavaScript packages.
In March, RL documented the discovery of NPM packages ethers-provider2 and ethers-providerz
Since discovering the ethers campaign, researchers have detected numerous additional infostealers, downloaders, and droppers found on NPM.
At the beginning of July, RL researcher Karlo Zanki discovered and reported a new NPM campaign involving a basic package that deployed blockchain in a novel way to deliver a malicious second stage.
The exact package colortoolsv2 is being used to infiltrate Ethereum smart contracts.
According to RL researchers, the malware is a basic NPM package containing just two files.
The major file is a script named index.js, which contains a hidden malicious payload.
Once installed in a project, the script would run to fetch blockchain data and execute a harmful command by loading the URL for a command and control (C2) server that would then download second-stage malware to the requesting system.
Although “downloader” malware is a common method hackers use in NPM repositories to target victims, this specific malware is unusual as it uses Ethereum smart contracts to host the URLs where malicious commands are located for downloading the second-stage malware.
Notably, the cybersecurity researchers acknowledge that they haven’t encountered this approach previously.
Two-File Malware Hides a $2.5M Bridge Exploit Method
The researchers uncovered a Solana-trading-bot infected by the malicious colortoolsv2 package called solana-trading-bot-v2, which appears to be a trustworthy GitHub project to the average observer.
It has thousands of commits, several active contributors, and a decent number of stars and watchers, all characteristics of legitimate open-source repositories.
However, all these details were fabricated, and any developer who installs it risks having user wallets that interact with the bot drained of funds.
Software supply chain attacks targeting smart contracts and blockchain infrastructure are now on the rise.
In July, hackers exploited a vulnerability in Arcadia Finance’s Rebalancer contract, draining approximately $2.5 million in cryptocurrency from the decentralized finance platform operating on Base blockchain.
The attackers manipulated arbitrary swapData parameters to execute unauthorized swaps that emptied user vaults.
A recent report by blockchain analytics firm Global Ledger revealed that hackers have now stolen $3 billion worth of crypto in 119 separate incidents during the first half of 2025, which is 150% more than all of 2024.
Slava Demchuk, CEO of analytics firm AMLBot, said access-control flaws and smart contract vulnerabilities, especially in bridges, continue to be dominant attack methods.
Demchuk told Cryptonews that these hackers are exploiting the interconnected and composable nature of decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to amplify the impact.
Blockchain auditors advised that it is critical for developers to assess each library they are considering implementing before deciding to include it in their development cycle.
Ayrıca Şunları da Beğenebilirsiniz

The Channel Factories We’ve Been Waiting For

Wyoming-based crypto bank Custodia files rehearing petition against Fed
