From trust mechanism to valuation logic, in-depth analysis of the subtle "father-son relationship" between L1 and L2
Author: taetaehoho, Eclipse CSO
Compiled by: Tim, PANews
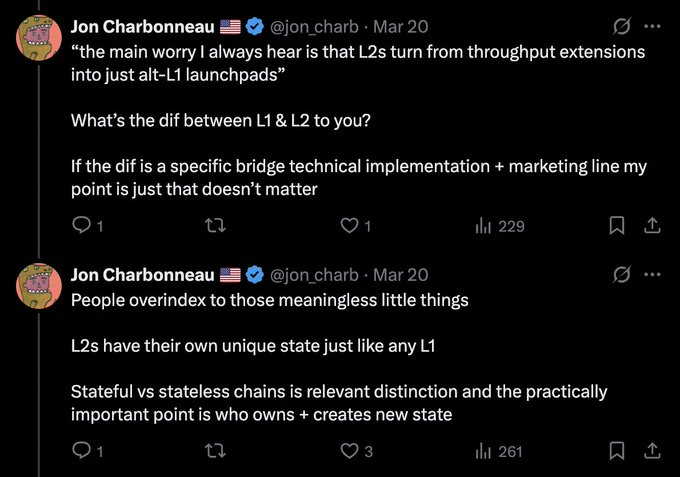
The tweet in the picture means: People are worried that L2 will change from a scaling solution to an L1 enabler, so what is the difference between L2 and L1?

The tweet in the picture means: The generational division of the chain in 2025 is outdated. There is no need to distinguish between L1 and L2. The real difference is the users and the ecosystem.
You should reread these tweets 100 times.
There is no product difference between L1 and L2 in terms of end-user perception. There is also no fundamental difference between L1 and L2 in terms of liquidity. A new L1 must be launched by bridging the liquidity of stablecoins or non-native assets to its chain. Similarly, an L2 also needs to be launched by bridging the liquidity of stablecoins or non-native assets to its chain. The difference between L2 is that it gets a trust-minimized bridge from L1, while Alt-L1 has no such mechanism but must rely on cross-chain message bridges. We have already seen that some whales are very sensitive to these trust assumptions, but many ordinary users don't care.
One view among the middle-of-the-road group (mainly from the Alt-L1 team) is that "L2 will lead to liquidity fragmentation."
One L2 only allows trust-minimized bridging from L1, but every L2 launched today will connect with Alt-L1 and other L2s.
Every L2 worth its salt will deploy a cross-chain message bridge when it launches. Any user connected to a base chain (such as Ethereum, Solana) can use this as a relay to transfer large amounts of assets between Alt-L1 and L2. If an Alt-L1 does not have its own L2, it may make it difficult for liquidity to flow outward, but if it also integrates a cross-chain message bridge, this creates a paradox.
The essence of an L2 product is not defined by its association with L1. It is simply an execution layer, just like any other execution layer with different characteristics.
So, why is L1 more valuable than L2?
Look at it from two perspectives.
1. Angle 1: Differences in the valuation logic of L1\L2 in the primary market and the secondary market
a. The valuation logic is the same in the secondary market
L1 has higher network activity. Solana/ETH is valued at ~100x annualized revenue, while mature L2s are in a similar range (10-200x). (Data from October 2024, but the argument still stands).
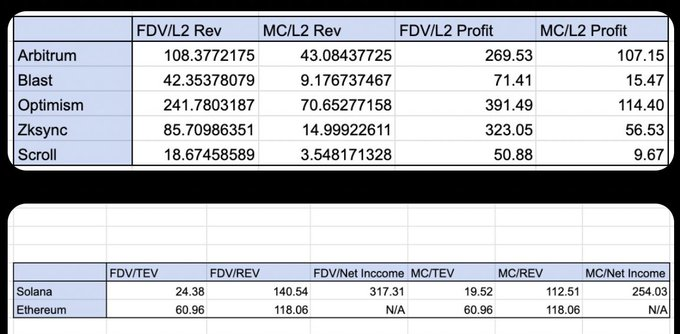
As indicated by fundamental valuation multiples, mature L1s and mature L2s are currently trading at relatively close valuation multiples (Arbitrum/Optimism vs. Solana/Ethereum).
b. Different valuation logic in the primary market
Compared with the secondary market, there are more unexplained extreme valuation multiples outliers in the primary market. In other words, there are projects with valuations of billions of dollars even though trading activity is not high. These phenomena tend to occur more in the primary market than in the secondary market.
Representative Projects
- L1: Sui, Mantra, Pi, ICP, IP (and many old projects from different periods)
- L2: MOVE
In my opinion, this is a misunderstanding of the initial L2 project in terms of framework setting. Arbitrum and Optimism position themselves as Ethereum's extended network, as an execution layer to help ETH expand. This positioning combined with Ethereum's "Rollup-centric roadmap" is indeed an excellent way to cold start.
But the disadvantage of this approach is that it limits the entire target market to the Ethereum user group, thereby limiting the overall liquidity, industry awareness, and revenue scale that these chains (such as Arbitrum/OP) can capture. Although Arbitrum and Optimism are fully capable of attracting new decentralized applications and ecosystem participants (including those who have never been involved in Ethereum), their initial go-to-market strategy (GTM) overemphasized themselves as "Ethereum's extended network." This positioning has led the market to always regard them as a subsidiary ecosystem of Ethereum (so the valuation is only seen as a percentage of Ethereum's value). To be honest, when these teams were launched, there was indeed only Ethereum, the mainstream ecosystem, in the market.
2. Angle 2: Token Model
An L1 token model has a fundamental network flywheel effect. When the L1 chain activity increases, it will directly drive the demand for tokens from two independent participants, namely on-chain speculators and stakers.
The more frequent the on-chain activity, the higher the fees on-chain speculators are willing to pay to include transactions in the block. The uncertainty brought by diversified activities increases the probability, frequency and scale of wealth opportunities, triggering people to compete for these opportunities. In terms of staking, the more fees a blockchain earns, the more people are willing to stake its native tokens to gain exposure to this part of the economic benefits. In addition, on-chain activities are often related to the issuance of net new assets, which are usually traded in pairs with native tokens. People need to buy these native tokens to participate in related trading activities (such as minting NFTs with ETH and buying Meme coins with SOL).
How should L2 deal with these problems?
Change your mindset
What L2 needs to decide clearly is: do you want to be an L2 focused on ecological collaboration, or do you want to attract users from any source? The construction of L2 should make full use of its unique second-layer technology advantages (trusted/customized block construction, performance optimization, and shareable profits).
Optimizing the token economic model
L2 should optimize its token economic model to form a flywheel effect where the growth of network activity can stimulate token demand on both the supply and demand sides. The current L2 attempt to use custom gas tokens has solved the incentive problem of on-chain speculation, but has failed to allow stakers to share this part of the revenue. In theory, since most L2s put the sorter revenue into the DAO treasury, and the token controls the DAO treasury, this is equivalent to distributing fair expectations of revenue to token holders. However, to achieve the same effect at the cognitive level of token holders, token holders must be given more complete governance rights.
Ayrıca Şunları da Beğenebilirsiniz

TRX Price Prediction: TRON Eyes $0.30-$0.35 Range as Technical Setup Improves

XLM Price Prediction: Stellar Eyes $0.30 Breakout Despite Current Bearish Momentum – December 2025 Forecast
