Medical Image Synthesis: S-CycleGAN for RUSS and Segmentation
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Related works
-
Problem setting
-
Methodology
4.1. Decision boundary-aware distillation
4.2. Knowledge consolidation
-
Experimental results and 5.1. Experiment Setup
5.2. Comparison with SOTA methods
5.3. Ablation study
-
Conclusion and future work and References
\
Supplementary Material
- Details of the theoretical analysis on KCEMA mechanism in IIL
- Algorithm overview
- Dataset details
- Implementation details
- Visualization of dusted input images
- More experimental results
4. Methodology
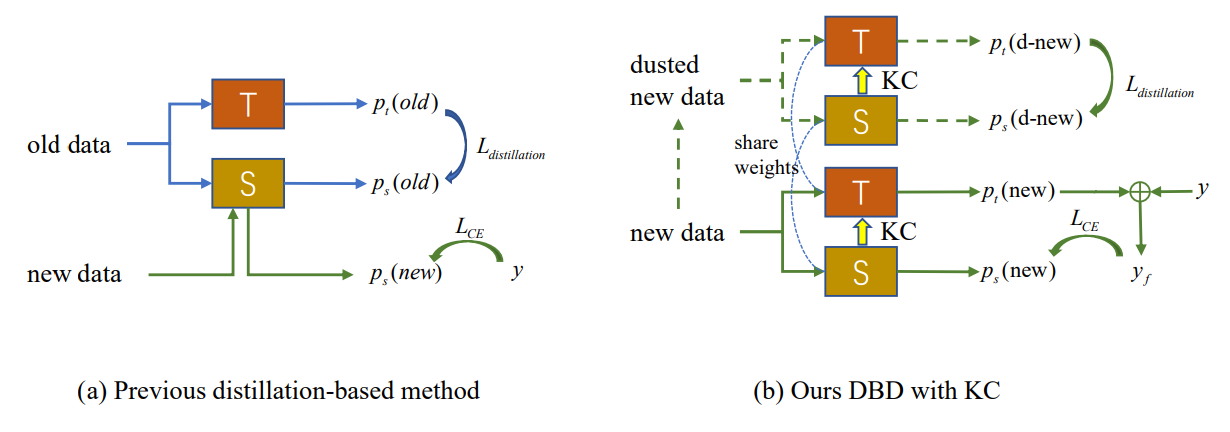
As shown in Fig. 2 (a), the occurrence of concept drift in new observations leads to the emergence of outer samples that the existing model fails on. The new IIL has to broaden the decision boundary to these outer samples as well as avoiding the catastrophic forgetting (CF) on the old boundary. Conventional knowledge distillation-based methods rely on some preserved exemplars [22] or auxiliary data [33, 34] to resist CF. However, in the proposed IIL setting, we have no access to any old data other than new observations. Distillation based on these new observations conflicts with learning new knowledge if no new parameters are added to the model. To strike a balance between learning and not forgetting, we propose a decision boundary-aware distillation method that requires no old data. During learning, the new knowledge learned by the student is intermittently consolidated back to the teacher model, which brings better generalization and is a pioneer attempt in this area.
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Qiang Nie, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou);
(2) Weifu Fu, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(3) Yuhuan Lin, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(4) Jialin Li, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(5) Yifeng Zhou, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(6) Yong Liu, Tencent Youtu Lab;
(7) Qiang Nie, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou);
(8) Chengjie Wang, Tencent Youtu Lab.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
Ayrıca Şunları da Beğenebilirsiniz

The Bold Move Signaling Unshakable Crypto Confidence

Kraken Lists Solv Protocol: A Strategic Boost for DeFi Liquidity
