Hackers Unleash Devious Malware That Steals Crypto Wallet Data Via Fake Captcha: Report
A new research brief published by DNSFilter indicates a rising threat to cryptocurrency users from fake CAPTCHA pages, which use deceptive “I’m not a robot” prompts to deliver malware targeting crypto wallets.
According to DNSFilter, the malicious activity was first identified by one of its managed service provider (MSP) customers. What initially appeared to be a routine CAPTCHA verification was, in fact, an attempt to deploy Lumma Stealer, a fileless malware strain capable of exfiltrating browser-stored credentials and wallet information.
While DNSFilter’s content filtering successfully blocked the attack, its researchers traced the infrastructure to reveal broader patterns of coordinated phishing efforts.
Fake CAPTCHA Scam Targets Greek Bank Users, Delivers Lumma Stealer via PowerShell Trick
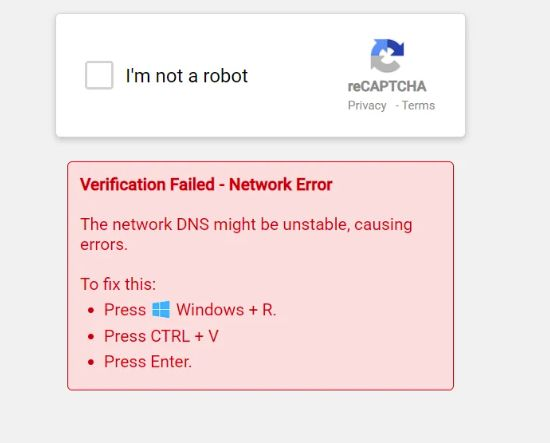
The incident began when users encountered a CAPTCHA overlay on a Greek banking site. The page mimicked a legitimate CAPTCHA but displayed a message claiming a DNS “network error,” instructing users to press Windows + R, paste a command from the clipboard, and hit Enter.
Following these steps would silently execute the Lumma Stealer payload via PowerShell outside the browser while performing a DNS lookup.
 Source: DNSFilter
Source: DNSFilter
DNSFilter linked the campaign to two other domains: human-verify-7u.pages.dev, a Cloudflare Pages site that returns an error after the user clicks the button, and recaptcha-manual.shop, which executes commands outside the browser after users follow the prompts.
Further investigation, detailed in DNSFilter’s case study, revealed that the campaign was a sophisticated blend of phishing and malware delivery. Attackers relied on fileless execution techniques, using legitimate browser processes to deliver payloads without writing to disk.
DNSFilter deployed its content filtering and domain-blocking controls across the MSP’s network, preventing infections before any credentials or wallet data were compromised. Alerts and blocking policies were updated in real time, and the MSP conducted end-user education sessions to reinforce the dangers of interacting with suspicious CAPTCHA.
“The malware in this event was Lumma Stealer, delivered through a fake CAPTCHA in a deceptive malvertising chain. Had the analyst’s device been infected, the PowerShell payload could have disabled Windows AMSI and loaded Lumma DLL,” the report explains.
“The stealer immediately sweeps the system for anything it can monetize—browser-stored passwords and cookies, saved 2FA tokens, cryptocurrency-wallet data, remote-access credentials, and even password-manager vaults.”
Analysis showed that the fake CAPTCHA was accessed 23 times across the DNSFilter network in just three days. More troubling, 17% of users who encountered the page followed its copy‑and‑paste instructions, triggering the malware payload attempt. While DNSFilter prevented successful infections in this case, researchers noted the potential scale if left unchecked.
Rapid Laundering Leaves Scam Victims Powerless to Recover Stolen Crypto
Reports have revealed that cybercriminals are laundering stolen cryptocurrency at unprecedented speeds. At these rates, victims of fake CAPTCHA schemes are left with virtually no chance of recovering their funds.
As per the previous report, crypto hackers can now transfer stolen digital assets through laundering networks in under three minutes.
Elliptic’s data shows that by using automated laundering tools and decentralized exchanges (DEXs), hackers are executing the entire laundering process in a matter of minutes.
“This new speed makes real-time intervention nearly impossible,” the report warned.
Cybersecurity experts warn that the fake CAPTCHA scams are not just a concern for big firms but also for regular users, as they are often disguised as part of login portals or app installations and target ordinary internet users who may not suspect foul play until their wallets are drained.
“Bad actors take advantage of both the highs and lows of life,” said Ken Carnesi, CEO and co-founder of DNSFilter. “Any person at any organization has the same chance of encountering a malicious link. The standard cyber hygiene tips apply: use unique passwords, verify who you are ‘talking’ to before handing over credentials, and think before you click.”
The rapid laundering process worsens the impact. Victims often discover the theft too late. Law enforcement agencies find it hard to trace the stolen funds across multiple blockchains. Experts note, however, that when cybersecurity firms intervene promptly, all or some of the stolen funds can still be recovered.
“Speed is critical. Funds often can be recovered in whole or part if proper actions are taken within 24 to 72 hours,” Cameron G. Shilling, a cybersecurity expert, said in a publication.
As hackers continue to shorten laundering times, the risks for victims are expected to grow. “The arms race between cybercriminals and defenders is accelerating,” Elliptic concluded. “Speed is now the hackers’ greatest weapon.”
Ayrıca Şunları da Beğenebilirsiniz

Binance Whale Loses $11.58 Million as Bitcoin Crashes Below $86,000

Tom Lee: Crypto's Best Years Lie Ahead as Adoption Gap Reveals Massive Growth Potential
